Contents
Breast cancer in women
The breast cancer one of the most types of malignant tumors; It is considered the second most common cancer after lung cancer that causes death among women, and breast cancer can be defined as a malignant tumor that affects breast cells, and it can affect men and women, but women are considered more likely to have it compared to men. The number of men diagnosed with breast cancer reached nearly 2,400 men, while the number of women diagnosed with breast cancer reached nearly 250,000 in 2017 in the United States of America alone. [1] [2] [3]
Types of breast cancer
There are many types of breast cancer that affect women, and some of them are more common than others, and there may be more than one type at the same time, and among the most prominent of these types are the following: [3]
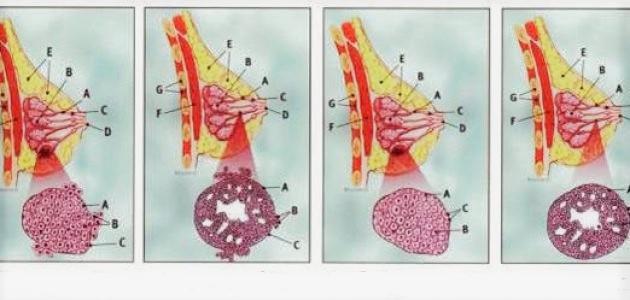
- Ductal carcinoma in situ: It is the most common type of non-invasive cancer that affects the breast, and it is characterized by a very high cure rate, due to the fact that it does not spread to the various tissues of the body, where it is concentrated in the breast cells, specifically the milk ducts .
- Invasive ductal carcinoma: It is the most common type of infiltrative cancer that affects the breast, as it accounts for 80% of the, and this type begins with the milk ducts in the breast, and then gradually spreads to the rest of the breast tissue.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma: This type makes up 10% of infiltrated carcinomas, and it begins in the milk-producing glands in the breast.
- Inflammatory breast cancer: This type of cancer is characterized by redness and warmth of the breast skin. These changes in the breast result from the blockage of the lymph ducts with cancer cells.
- Paget's disease of the nipple: Cancer cells begin to grow in this type inside the milk ducts, and then spread to the nipple and the area around it, where the area around the nipple appears red, in addition to the presence of cracks in the nipple And around.
- Mucinous carcinoma.
- Cancer myeloid .
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma.
- Lobular carcinoma in situ.
Factors that increase the risk of breast cancer
Although there is no clear cause yet for breast cancer, there are a number of factors that increase the risk of breast cancer, the most prominent of which are the following: [1]
- Age: A woman's risk of developing breast cancer increases as she gets older.
- Genetics: The more people with cancer from first-degree relatives the higher the incidence of breast cancer.
- Pathological history: If the patient has suffered from a lump in her breast, whether malignant or benign, then the incidence of breast cancer increases.
- Breast tissue density: The denser the breast tissue, the greater the chance of breast cancer.
- Weight: the more weight a female has after menopause, the greater the risk of infection.
- Hormonal replacement therapy and birth control pills.
- Alcohol intake.
- Exposure to radiation.
Signs and symptoms of breast cancer
There are a number of symptoms and signs that appear on women with breast cancer, and among the most prominent of these symptoms and signs are the following: [2]
- The presence of a lump in the breast or its increase in thickness to appear different from the surrounding tissues.
- Change in the size, shape or appearance of the breast.
- A change in the shape of the skin surrounding the breast, such as clicks.
- A change in the shape of the nipple.
- Crusting and erosion of the darkened area around the nipple.
- The presence of redness or holes in the skin of the breast, similar to the peel of an orange fruit.
Diagnosing breast cancer
Although the presence of some of the signs and symptoms mentioned above is a strong indicator of the presence of cancer, there are a number of tests that are used to diagnose cancer, and the most prominent of these tests are the following: [1]
- Clinical breast examination; Where the doctor examines the patient clinically to detect the presence of any lump in the breast.
- Mammogram, which is a type of X-ray, is used for the early detection of breast cancer.
- Ultrasound ; It can distinguish whether breast cancer is a solid or a fluid-filled cyst.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging ; It is used to assess the extent to which cancer has spread to the body or breast.
- Take a sample or biopsy ; Where a sample of breast tissue is taken using a dedicated needle, to find out whether this mass is a benign or malignant tumor.
Breast cancer treatment
Breast cancer treatment depends on the patient’s age and general health, as well as on the type of breast cancer, the stage it has reached, and the extent of its response to hormones. It can be said that among the most prominent treatment methods are the following: [1]
- Surgery: There are several types of surgical excision, including removing the tumor alone with some of the surrounding cells without completely removing the breast, removing some lymph nodes if necessary, and much more, and the surgical procedures aim to control cancer and prevent its spread.
- Radiation therapy: where a beam of rays is shed on the cancer cells to destroy them, and the patient may need from three to five sessions per week for a period not exceeding six weeks.
- Chemotherapy: This is done by taking some drugs that kill cancer cells.
- Biological therapy: where specialized drugs are taken to destroy a specific type of cancer cells in the breast.
References
- ^ A b T w Christian Nordqvist (27-11-2017), "What ' You Need To Know About Breast Cancer" , www.medicalnewstoday.com The , Retrieved 3-2-2018. Edited.
- ^ A b "Breast Cancer" , Www.mayoclinic.org , 17-1-2018, Retrieved 3-2-2018. Edited.
- ^ A b Jerry R for Balentine (26-6-2017), "Breast Cancer" , Www.medicinenet.com . Edited.