Contents
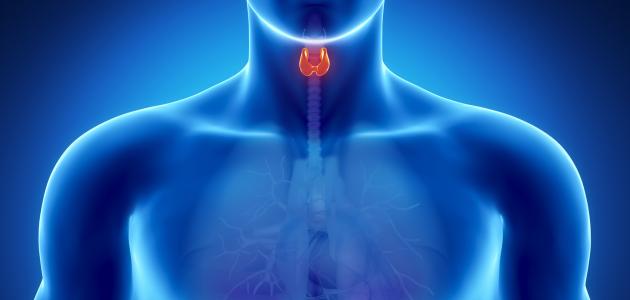
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism or hyperthyroidism can be defined as an increase in the production of the main thyroid hormones above the normal rate, which are the hormones responsible for regulating metabolic processes in the body, and hyperthyroidism is accompanied by a number of different symptoms; Such as weight loss, nervousness and irritability, feeling tired and fatigued, increased heart rate and disturbance , in addition to suffering from diarrhea, and sleep disturbances , and it is worth noting that hyperthyroidism is more common in women, and the elderly who are over 60 years old, and people Those with another thyroid disease. [1]
To learn more about hyperthyroidism, read the following article: ( What is the activity of the thyroid gland ) .
Causes of hyperthyroidism
There are many different reasons that may lead to suffering from hyperthyroidism, including the following:
Graver's disease
Graves 'disease is the most common cause of suffering from hyperthyroidism. [2] It is also known as exophthalmos because it is accompanied by bulging in the eyes of an affected person in some cases, and Graves' disease is one of the types of autoimmune disorders that It increases the production of thyroid hormones, as the immune system builds upIn the body by producing a number of abnormal antibodies in the body, such as: Thyrotropin receptor antibody (TRAb), which in turn inhibit the action of the pituitary hormones responsible for regulating the production of thyroid hormones , Which leads to an increase in the percentage of its production exceeding the normal rate, and scientists have not been able to determine the main cause of Graves' disease until now, but there are a number of risk factors that may increase the chance of contracting the disease, and the following are some of them: [3] [4]
- Family health history: The chance of developing Graves' disease increases if there is a family history of the disease, as it is believed that there are genetic factors that may be responsible for the disease.
- Gender: Women are more likely to have Graves' disease than men.
- Age: As Graves' disease occurs in most cases before the age of forty.
- Infection with one of the other autoimmune diseases: such as Rheumatoid arthritis and Type 1 diabetes.
- Exposure to one of the triggers of the disease: The risk of developing Graves' disease increases if people who have one of the genetic traits responsible for developing the disease are exposed to some of the triggers. Such as infection with some types of infections, the use of some types of drugs, exposure to psychological and physical stress, pregnancy, smoking, and exposure to radiation therapy in the neck area.
Overactive thyroid nodules
Abnormal growth of some nodules may occur within the thyroid gland, which does not affect the nature of the thyroid gland's work in most cases, but some of these nodules, such as those known as hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules, produce thyroid hormones Excessively without responding to the hormones of the pituitary gland, which are responsible for regulating the production of thyroid hormones, leading to hyperthyroidism. [5] [6] Overactive thyroid nodules are divided into several different types, including the following:
Toxic thyroid tumor
Toxic adenoma is the overproduction of thyroid hormones within one nodule of the thyroid gland caused by a benign tumor that is usually more than 2.5 centimeters in size, which leads to what is known as thyrotoxicosis. [7]
Poisonous nodule goiter
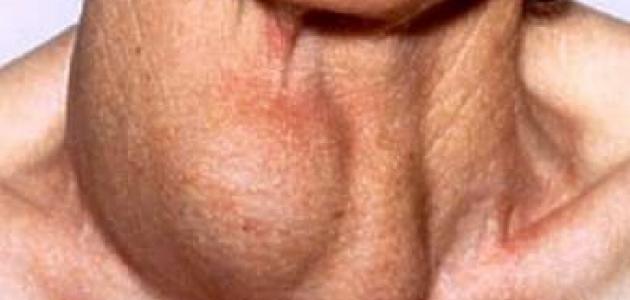
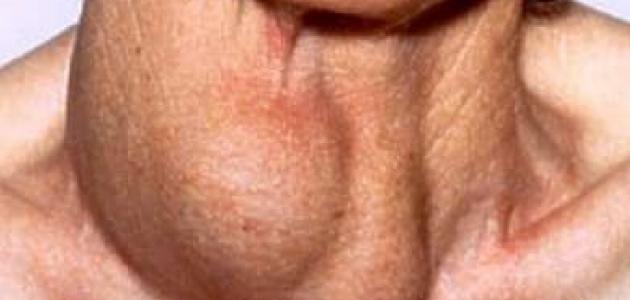
A multinodular goiter is characterized by an enlargement of the thyroid gland as a result of the growth of several nodules in it. The symptoms of Plummer's disease are characterized by an enlarged thyroid gland before the symptoms of hyperthyroidism appear, and the affected person may suffer from an excessive enlargement of the thyroid gland in some cases, which in turn may lead to difficulty breathing or swallowing, which requires surgery to remove part of the thyroid gland. An enlarged tissue in the gland. [8] [9]
Plummer's disease occurs as a result of a deficiency of iodine in a person's diet, which is the component used by the thyroid gland to produce its hormones, which in turn leads to an enlarged thyroid gland in an attempt to increase the ability to absorb iodine from the blood and increase its production capacity, and it should be noted that this type of infection Of nodules are more common with age, especially in areas of high prevalence of iodine deficiency. [9]
Receiving large amounts of thyroid hormones
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism may be caused by taking a large dose of thyroid hormones, and this condition is known as Factitious hyperthyroidism, and this condition often occurs as a result of obtaining thyroid hormones from several different sources within a short period of time; Such as using Levothyroxine with some other natural remedies that contain thyroid hormones; Such as plant or animal sources that contain this hormone, as this may cause what is known as overmedication; This condition is represented by obtaining a high dose of the drug Levothyroxine used in the treatment of hypothyroidism , and there are a number of possible reasons that may lead to this problem, we show the following: [10] [11]
- The doctor has prescribed an overdose of the medicine, or the failure to attend to the doctor to regulate the dose of the medicine after it has been prescribed.
- Alter the pharmaceutical form used for the drug; Like moving from pill use to the liquid form of medication.
- Using the wrong dose of medicine that does not match the instructions of the doctor, or not following the instructions of the doctor or pharmacist about the correct way to use the medicine.
Thyroiditis
There are a number of different health disorders that may lead to inflammation of the thyroid gland , and this inflammation results in a number of different symptoms depending on the type of inflammation that occurs in the gland, and in general, inflammation of the thyroid gland may lead to suffering from its overactivity, or Its deficiencies, and the most prominent types of thyroiditis that may lead to its overactivity can be explained as follows: [12] [13]
- Inflammation of the thyroid gland have Quervain: , as is the incidence of this type of inflammation of the most common thyroid gland in women between the ages of 20-50 years old, swollen and is painful in the thyroid gland, suffering from fever, pain in both The neck, jaw, and ear, and scientists believe that infection with this type of thyroiditis is caused by infection with some types of viral infection, and in some cases it may lead to an increase in the activity of the thyroid gland for several days with the emergence of symptoms of hyperactivity of the gland, then followed by the emergence of symptoms of insufficiency The thyroid gland for several weeks or months in a row before the gland returns to its normal activity.
- Thyroiditis caused by drugs: The use of some types of drugs may cause damage and inflammation to the thyroid gland, which in turn may lead to insufficient or overactive thyroid gland, and this effect often disappears after stopping the use of the drug, and among these drugs is the drug Amiodarone ( In English: Amiodarone, Lithium, and Interferon.
- Thyroiditis caused by exposure to radiation: Exposure of the thyroid gland to radiation therapy used to control some types of cancers and hyperthyroidism may cause damage and inflammation in this gland, which in turn may lead to suffering from an overactive or deficient gland activity.
- Inflammation of the thyroid gland silent: , this type of inflammation of the thyroid gland occurs as a result of injury to one autoimmune disease, and may also lead to suffering from excessive activity of the thyroid , followed by a lack of activity, and in many cases , restore the thyroid gland normal activity Within a period of 12-18 months, about 20% of cases turn into permanent suffering from hypothyroidism.
- Postpartum thyroiditis : In several rare cases, some women may suffer from postpartum thyroiditis, which may be caused by the immune system attacking the thyroid gland approximately 6 months after birth, which leads to adenitis Leaking of a large proportion of her hormones into the bloodstream, and this type of gland inflammation is usually accompanied by pain, and due to the loss of large quantities of hormones in the gland, this case follows a stage of hypothyroidism, and in most cases the woman returns to the normal activity of the gland within a year of birth. [13] [14] To learn more about postpartum thyroiditis, read the following article: ( Postpartum thyroiditis ) .
Other reasons
Pituitary tumor
A tumor in the pituitary gland may lead to an overproduction of the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which in turn leads to an overstimulation of the thyroid gland to produce hormones, and it should be noted that this condition is one of the cases. Very rare, and it is called TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma; It is a slow-developing polyp. [3] [15]
Thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer can be defined as cancer that arises within one of the different types of thyroid cells, and this type of cancer is divided into several different types. Such as Hürthle cell carcinoma, Anaplastic thyroid cancer, and Medullary thyroid carcinoma, and the causes of thyroid cancer vary according to its type, and these causes may be hereditary, or It may arise as a result of iodine deficiency in the diet in some countries, or it may have an unknown cause. [16] [17]
To learn more about thyroid cancer, read the following article: ( thyroid cancer ) .
Iodine consumption in large quantities
The thyroid gland works to cope with the consumption of large amounts of iodine through what is known as the Wolff-Chaikoff effect in most cases, but in some cases, exposure to a high level of iodine may lead to suffering from what is known as hyperactivity. Thyroid activity caused by iodine -induced hyperthyroidism, and this condition occurs in some people who suffer from an undiagnosed thyroid disease, or in people who move from an area that suffers from iodine-induced hyperthyroidism. Rich in iodine, this phenomenon is known as the Jod-Basedow phenomenon. [18]
Use of some types of medication
The use of certain types of drugs may lead to suffering from drug-induced hyperthyroidism, and this may be due to the effect on the metabolism of thyroid hormones, their absorption in the body, or the speed of their production, as it may Some medications affect the thyroid stimulating hormone level and may lead to a decrease in the thyroid gland. What leads to an overactive thyroid gland, and drugs that may lead to an overactive thyroid gland are amiodarone, interferon, tyrosine-kinase inhibitor, and iodine-containing drugs. [19]
Thyroid hormones
In fact, the thyroid gland produces two main types of hormones. These are the hormone triiodothyronine , short for T3, and the hormone thyroxine and for short T4, and the thyroid gland needs sufficient amounts of iodine in order to be able to manufacture these hormones, and it is indicated that the amount of hormones that the thyroid gland makes is usually They are tightly regulated, as this is done through the hypothalamus, which sends signals to the pituitary gland to produce a hormone known as Thyroid stimulating hormone, as this hormone directs its signals to the pituitary to control the production of its hormones, [20] and is referred to as When hyperthyroidism is diagnosed, blood tests show an increase in the levels of both the hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine, while the thyroid stimulating hormone is low. [21]With regard to the normal range of the level of these hormones, it comes as follows: [22]
- Thyroid stimulating hormone: between 0.4-4mIU per liter.
- Free THR : between 9-25 picomol per liter.
- Free thyroxine: between 3.5-7.8 picomol per liter.
References
- ↑ "Hyperthyroidism" , medlineplus.gov , Retrieved 18-9-2019. Edited.
- ↑ "Graves' Disease Causes" , www.endocrineweb.com , Retrieved 18-9-2019. Edited.
- ^ A b of Melissa Stöppler of Conrad, "Hyperthyroidism Definition And Facts" , Www.medicinenet.com , Retrieved 6-9-2019. Edited.
- ↑ "Graves' disease" , www.mayoclinic.org , 6-3-2018, Retrieved 18-9-2019. Edited.
- ↑ "Thyroid Nodule" , my.clevelandclinic.org , Retrieved 9-18-2019. Edited.
- ↑ "Thyroid nodules" , www.mayoclinic.org , 18-2-2017, Retrieved 18-9-2019. Edited.
- ↑ "What causes toxic adenoma" , www.medscape.com , Retrieved 18-9-2019. Edited.
- ↑ Rachel Nall, “What to know about multinodular goiter” , www.medicalnewstoday.com , Retrieved 9-18-2019. Edited.
- ^ A b "Toxic Thyroid Nodule" , Www.yourhormones.info , Retrieved 18-9-2019. Edited.
- ↑ Yashpal Agrawal, "Factitious Hyperthyroidism" , www.cancertherapyadvisor.com , Retrieved 9/18-2019. Edited.
- ↑ Mary Shomon (2-7-2019), "Are You Taking Too Much Thyroid Medication?" , Www.verywellhealth.com , Retrieved 18-9-2019. Edited.
- ↑ "Thyroiditis" , www.thyroid.org , Retrieved 18-9-2019. Edited.
- ^ A b "Thyroiditis" , Www.nhs.uk , Retrieved 18-9-2019. Edited.
- ↑ "Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid)" , www.mayoclinic.org , 3-11-2018, Retrieved 9-18-2019. Edited.
- ↑ "TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma" , www.yourhormones.info , Retrieved 18-9-2019. Edited.
- ↑ "What Is Thyroid Cancer" , www.cancer.org , Retrieved 18-9-2019. Edited.
- ↑ Kristin Della Volpe, "Is There a Link Between Thyroid Cancer and Hyperthyroidism" , www.endocrineweb.com , Retrieved 6-9-2019. Edited.
- ↑ Ruchi Mathur, "Thyroid & Iodine" , www.medicinenet.com , Retrieved 18-9-2019. Edited.
- ↑ Michel Procopiou, Christoph A. Meier, "Effects of drugs on thyroid function tests" , www.endocrinologyadvisor.com , Retrieved 9/18-2019. Edited.
- ↑ "Thyroid gland and thyroid hormones" , www.mydr.com.au , Retrieved 18-9-2019. Edited.
- ↑ "Hyperthyroidism" , www.ucsfhealth.org , Retrieved 18-9-2019. Edited.
- ↑ "Thyroid Function Tests" , www.btf-thyroid.org , Retrieved 9-18-2019. Edited.