Contents
Hemorrhoid symptoms
General symptoms
Hemorrhoids do not cause any pain or other symptoms in most cases, but in the event that symptoms appear, the patient may suffer from the following: [1]
- Bleeding during a bowel movement, which is the most common symptom of hemorrhoids. The patient may notice pink blood on the toilet paper, in the toilet, or on the surface of the stool, [2] [2] This bleeding is not accompanied by any pain, [3] and the amount of blood is small. [4]
- An abscess or aperture from the anus. [2]
- Feeling of discomfort in the anus, or a feeling that the bowel has not completely emptied after bowel movements. [2]
- Lumps and swelling in the anal area. [3]
- Itching and irritation in the anal area. [3]
- Feeling of discomfort and discomfort in the anal area. [3]
It should be noted that rubbing the area around the anus and cleaning it hard and exposing it to stress may aggravate the symptoms. [5]
Hemorrhoid symptoms by type
Symptoms depend on the type of hemorrhoids, and they are as follows: [1]
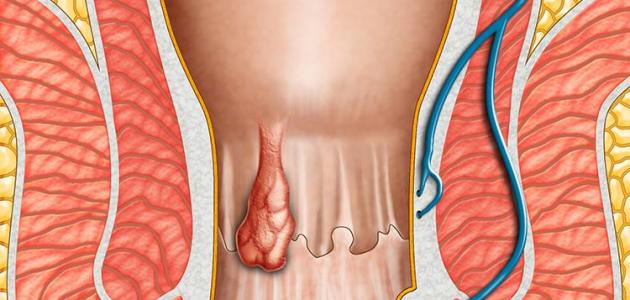
- Internal hemorrhoids: Internal Hemorrhoids appear in superficial areas of the upper part of the anal canal. Temperature changes, and in some cases, internal hemorrhoids may coagulate outside the anus. [6] [7] Often internal hemorrhoids do not appear, and it is rare for pain, fatigue or irritation when passing stool leads to profuse bleeding. [8]
- External hemorrhoids: external hemorrhoids show near the anus and specifically at 2 to 3 inches in the anus, and covered by a layer of skin, called external hemorrhoids name because it is hanging outside the anus, [6] [7] and symptoms Certain external hemorrhoids can be stated as follows: [8]
- Rash in the anal area.
- Feeling of pain and discomfort.
- Bleeding
- Swelling around the anus.
- Hemorrhoids thrombotic: , which is one of the types of hemorrhoids that have Mottaglta blood inside and therefore does not flow in which blood, and often these external hemorrhoids , but they may be internal in some cases, which is not dangerous, [9] and accompanied by a group of Symptoms:
- Feeling severe pain, [8] and this pain is caused by a blood clot, and it begins within 48-72 hours of the formation of the clot, and usually the intensity of pain subsides on the fourth day of feeling the pain, and in the event that the pain is present without the appearance of hemorrhoids, the cause of this pain must be searched It may be caused by an anal fissure. [10]
- Infections. [8]
- Swelling of the area. [8]
- The appearance of a hard lump in the anus. [8]
See a doctor
It should be noted that hemorrhoids disappear on their own without using any treatment, or by using simple treatments, so it is necessary to see a doctor in the event that symptoms persist after a week of using the treatment, or if pain is felt, or if there is bleeding during the bowel process, as The bleeding may be caused by another health condition, especially if there are changes in bowel movement, or if the color or consistency of the stool has changed [11] [8] . Suffering from lightheadedness, dizziness or fainting. [8]
Diagnose hemorrhoids
The doctor diagnoses hemorrhoids by taking the patient’s medical history and performing a clinical examination. [12] The examination is done by wearing medical gloves and examining the rectum and anus by inserting his finger into the anus, [13] or by using a short, lighted endoscope inside the anus. [12] .
Medical history
The doctor asks the concerned person about his family’s medical history and asks him to describe the symptoms he is suffering from, and among the most important points that the doctor addresses is the patient’s food habits, the way he used the toilet to relieve himself, and whether he used laxatives and enema, and he is also interested in knowing Other health problems he suffers from. [14]
Physical examination
Hemorrhoids are divided into external hemorrhoids and internal hemorrhoids , and they can be differentiated through a physical examination, as external hemorrhoids are easily diagnosed by looking, while internal hemorrhoids require an anal examination, [15] and from The most important things that the doctor is concerned with observing are the following: [16]
- Lumps or swelling and swelling in the area.
- Hemorrhoids prolapse through the anus.
- Knowing about external hemorrhoids that are accompanied by the presence of a blood clot in the blood vessels.
- Stool leakage or mucus.
- Dermatitis.
- Skin growths and blood clots associated with external hemorrhoids when they resolve.
- Anal fissures are small tears in the anus that may itch, pain, or bleed.
Endoscopy and other medical tests
In some cases, the doctor requests tests that enable viewing the anus and even the lower part of the colon, to confirm the diagnosis of hemorrhoids, and these tests include the following: [17]
- Anoscopy: , and helps to diagnose internal hemorrhoids, [18] and is done using a tool known lens anal where it is entered there, [19] This tool is only a short solid hollow tube dedicated for this purpose, through which disclosure About 5 centimeters in the anal canal, and the good thing about this examination is that it can be performed at any time because it does not need preparation. [17]
- Endoscopic rectal: , the length of this tool is mostly 25-32 cm, width 2.5 cm, and from which to see the rectum, and often requires the preparation of this examination procedure. [17]
- Colonoscopy sigmoid: This requires examination taking laxatives or enemas. [20] [17]
- Complete colonoscopy: , in which the colonoscopy is performed by examining all its parts. [20]
- X - ray examination Balbarbom: , this assay is by taking an injection Barium (Balangelazbh: barium enema) and then radiation technician taking X - ray image of the lower part of the colon. [20]
To learn more about the diagnosis of hemorrhoids, you can read the following article: ( How do you know that you have hemorrhoids ) .
To learn more about hemorrhoids, you can read the following article: ( Hemorrhoids Disease ) .
References
- ^ A b "Haemorrhoids (Piles) - Symptoms And Treatment" , Www.southerncross.co.nz , Retrieved 24-7-2020. Edited.
- ^ A b t w "Piles (Haemorrhoids)" , Www.bupa.co.uk , Retrieved 24-7-2020. Edited.
- ^ A b t w "What ' To Know About Hemorrhoids" , www.medicalnewstoday.com The , Retrieved 28-7-2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Patient education: Hemorrhoids (Beyond the Basics)" , www.uptodate.com , Retrieved 7-31-2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Diagnosis of Hemorrhoids" , www.niddk.nih.gov , Retrieved 7/31-2020. Edited.
- ^ A b "Piles" , Patient.info , Retrieved 24-7-2020. Edited.
- ^ A b "Hemorrhoids: the Expanded . Version" , Fascrs.org , Retrieved 24-7-2020. Edited.
- ^ A b t w c h x d "Hemorrhoids" , Www.mayoclinic.org , Retrieved 28-7-2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Thrombosed Hemorrhoid Symptoms and Treatment" , www.verywellhealth.com , Retrieved 7-28-2020. Edited.
- ↑ "What are the signs of haemorrhoids?" , www.exroid.com , Retrieved 28-7-2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Haemorrhoids (piles)" , www.nhsinform.scot , Retrieved 7-31-2020. Edited.
- ^ A b Healthwise Staff (7/11/2018), "Hemorrhoids" , Healthlinkbc , Retrieved 4/7/2020. Edited.
- ↑ Ronald Bleday (5/13/2019), "Patient education: Hemorrhoids (Beyond the Basics)" , uptodate , Retrieved 4/7/2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Diagnosis of Hemorrhoids" , www.niddk.nih.gov , 10/2016 , Retrieved 5/7/2020. Edited.
- ↑ By Mayo Clinic Staff (3/7/2019), "Hemorrhoids" , www.mayoclinic.org , Retrieved 5/7/2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Diagnosis of Hemorrhoids" , www.niddk.nih.gov , 10/2016 , Retrieved 5/7/2020. Edited.
- ^ A b t w Healthwise Staff (21/8/2019), "Sigmoidoscopy (Anoscopy, Proctoscopy)" , Www.uofmhealth.org , Retrieved 16/7/2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Hemorrhoids" , medlineplus.gov , 6/8/2020 , Retrieved 7/16/2020. Edited.
- ↑ Amber J. Tresca (7/7/2019), "How Hemorrhoids Are Diagnosed" , www.verywellhealth.com , Retrieved 7/16/2020. Edited.
- ^ A b v Laura J. Martin (9/6/2019), "How To Hemorrhoids are On Diagnosed And Tested?" , The www.webmd.com , Retrieved 8/7/2020. Edited.