Contents
Malaria
Malaria is defined as one of the dangerous diseases that may lead to death, causing the death of approximately 445 thousand people annually, most of them in Africa. Anopheles mosquitoes), and malaria causes high fever and chills that may threaten the life of the infected person, and malaria spreads in areas with warm and hot climates, such as: Latin America, the Middle East, sub-Saharan Africa, and Southeast Asia, and it can be transmitted to regions Others, via travelers, or immigrants from these countries. [1]
Methods of infection with malaria
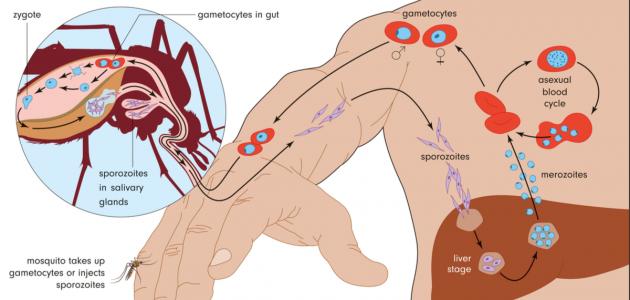
A microscopic parasite causes malaria, as this parasite is transmitted to humans through mosquito bites, and the way malaria is transmitted by mosquitoes can be explained as follows: [2]
- The mosquito feeds first on the blood of a person with malaria, then becomes a vector mosquito.
- Transmission of this mosquito parasite when pinched to another uninfected person.
- The parasite enters the body and goes directly to the liver ; It could remain there in a dormant state for a year.
- The parasite leaves the liver after maturing, and goes to the bloodstream, to attack the red blood cells there, and from here the symptoms of malaria begin to appear.
- The possibility of increasing the chance of infection of other people with malaria if the patient is bitten by a mosquito that does not transmit malaria, and among other ways of transmitting malaria is the following:
- Sharing needles used to inject medications.
- Transfer from mother to fetus.
- Transmission by blood transfusion .
Types of the malaria parasite
There are many types of plasmodium , including five types that cause malaria, which are: [3]
- Plasmodium vivax : During the dormant stage, it can cause relapses, and it spreads in Latin America and Asia.
- Plasmodium knowlesi : the uncomplicated symptoms turn into a more severe condition quickly, and this type spreads in Southeast Asia.
- Plasmodium ovale : is found in Africa and the Pacific Islands.
- Plasmodium malariae : causes a chronic infection and is spread throughout the world.
- Plasmodium falciparum : It contributes to raising the number of deaths from severe malaria, and it is spread in tropical and subtropical areas.
Symptoms of malaria infection
The appearance of symptoms needs a period ranging between 7-30 days, and this period is called the incubation period, and there are many symptoms that appear when infected with malaria, as they have been divided into complex symptoms and uncomplicated symptoms, and examples of uncomplicated symptoms when infected with malaria are the following: [4]
- Fever and chills .
- Have a headache.
- General weakness and pain in the body.
- Feeling sick and vomiting .
As for the severe and complex symptoms, they occur when malaria attacks various parts of the body, and among these symptoms are the following: [4]
- Incidence of anemia , severe result of the breaking of red blood cells.
- Kidney failure.
- Exposure to hypoglycemia in pregnant women who use quinine for treatment.
- Worsening heart and blood vessel health.
- Cerebral malaria ; It leads to seizures, disorientation, and loss of consciousness.
Diagnose malaria
The disease is diagnosed by a specialist doctor. Where he looks at the patient’s medical history, and whether the patient has traveled to tropical areas and places of spread of the disease, and the doctor makes sure that an enlarged liver or spleen does not occur , but in the event that symptoms of malaria appear, the doctor requests a blood examination for several goals, including: [5 ]
- Proof of malaria.
- Determine the type of malaria.
- Find out if the parasite causing malaria has resistance to certain drugs.
- Confirm the chance of developing anemia due to malaria.
- Find out if there are internal organs affected by the disease.
Malaria treatment
The goal of treating malaria is to get rid of the plasmodium parasite from the bloodstream, and the World Health Organization recommends the use of artemisinin to treat uncomplicated malaria, and artemisinin is extracted from the sweet wormwood plant , as it has the ability to Reducing the numbers of the parasite in the blood, and doctors give other drugs besides artemisinin, as artemisinin helps to reduce the numbers of the plasmodium parasite in the first three days of infection, while the other drug eliminates what is left of the parasite, and artemisinin has become one of the most used drugs to treat malaria around the world However, many cases of the disease have emerged resistant to artemisinin, prompting the use of stronger drugs with artemisinin, and the World Health Organization warns that there is no alternative to artemisinin for several years. [6]
Prevention of malaria
Researchers seek to find a vaccine to prevent malaria , as the vaccine will be one of the most important ways to prevent malaria in the future, and one of the advice followed to prevent the disease is to avoid mosquito bites that transmit malaria, through the following: [7]
- Use mosquito nets and bed nets, and it is best to spray insect repellents on these nets, such as: permethrin .
- Wearing clothes that cover the entire body.
- Staying at home, especially at night. Because it is the preferred time for the activity of the malaria mosquito.
- Spray permethrin on clothes.
- Use an insect repellent that contains icaridin (Picaridin) or DEET, and put it on the skin except for the areas around the mouth and eyes, and reapply it every few hours if using icaridine.
Some medicines can be used to prevent disease if you travel to areas where malaria is spread, and these medicines include the following: [7]
- Chloroquine : It is one of the most common medicines used in areas where there is no resistance to malaria , and the medicines are taken once a week two weeks before travel, and continue to be taken even after returning from travel for four weeks, and this medicine can cause dizziness and itching Feeling nauseous; Therefore, it is preferable to take the medicine after eating.
- Mefloquine : The use of mefloquine is common in areas where there is resistance to chloroquine, such as: sub-Saharan Africa. Mefloquine is taken once a week two weeks before travel, and it continues to be taken four weeks after travel. Feeling dizzy, hallucinations, nightmares, seizures, and nausea; Therefore, this drug is not indicated for patients with convulsions, and for patients who have neurological or psychological problems, and who have disturbances in the ECG .
- Doxycycline: Doxycycline is given to patients who cannot take mefloquine or chloroquine, and it is taken once a day. It starts with two days before travel, and continues until four weeks after returning from travel, and this drug exposes the skin to sensitivity from sunlight. Therefore, the skin must be protected from the sun's rays, and it is worth noting that the administration of doxycycline to children and pregnant women should be avoided.
References
- ↑ "What Is Malaria and What Are the Symptoms?" , www.webmd.com , Retrieved 18-5-2019. Edited.
- ↑ "Malaria" , www.mayoclinic.org , Retrieved 18-5-2019. Edited.
- ↑ Jerry R for Balentine, the DO, FACEP, "Malaria" , Www.medicinenet.com , Retrieved 22-5-2019. Edited.
- ^ A b "MALARIA" , Www.rxlist.com , Retrieved 18-5-2019. Edited.
- ↑ Darla Burke, "Malaria" , www.healthline.com , Retrieved 22-5-2019. Edited.
- ↑ Peter Lam, “What to know about malaria” , www.medicalnewstoday.com , Retrieved 22-5-2019. Edited.
- ^ A b "Malaria" , Www.drugs.com , Retrieved 20-5-2019. Edited.