Polycystic, not ovarian cysts
A disease in the ovaries that causes an imbalance of ovulation due to an imbalance of hormones.
It is sometimes associated with other symptoms (such as menstrual irregularity, weight gain, the appearance of coarse hair and acne in different areas of the woman's body, and a lack of head hair) and is called (PCOS). Sometimes it does not have any symptoms and is discovered by chance upon examining the patient for another reason.
Contents
Spread
It is very common and differs from country to country and race to race. In general, it is at a quarter to a third of women.
the reasons
The exact causes are unknown, and it is believed that there is a hereditary nature of the disease (it abounds in some families and relatives). It starts in the teenage years when rapid weight gain and hormonal changes occur.
There may be some role for insulin receptors, and some medications (such as antiepileptic drugs) may cause symptoms.
Symptoms and signs
It is very variable and the disease can be discovered by chance.
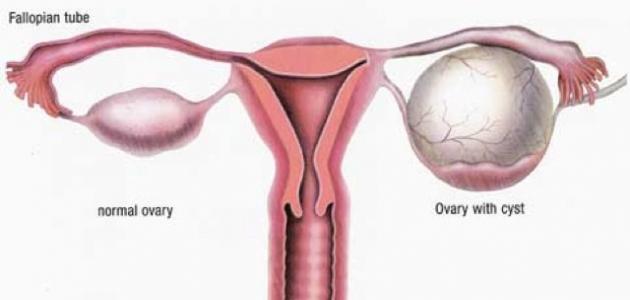
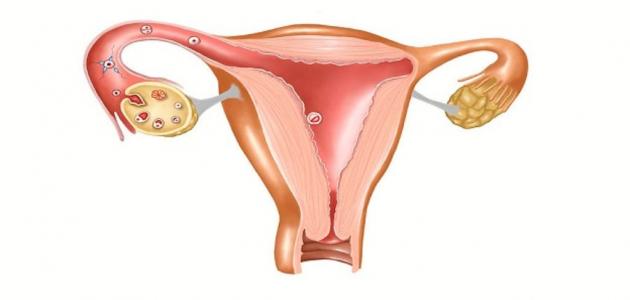
Sonar: The presence of 10 eggs, each of less than 10 mm in size, in the vicinity of the ovary (such as pearl necklace beads). The ovary is enlarged one and a half to three times and the ovarian tissue increases in the middle.
Symptoms
1- Menstrual disorder: interruption or spacing of periods.
2- Poor ovulation: it causes delayed pregnancy and infertility.
3- Weight gain: The body mass index (BMI) is more than 30. The weight gain is concentrated in the trunk, which causes a disturbance of body fat.
4- The appearance of coarse hair in different areas of the woman's body, including the chin, the mustache area, the
abdomen and the chest, due to the male hormone disorder.
5- Acne increases, especially on the face and back, and the skin becomes oily.
6- Frequent miscarriage due to high LH.
7- There may be high blood pressure and diabetes.
Causes of symptoms and diagnosis
Hormonal changes are not fully known, but there is an increase in the hormone insulin in many patients. This hormone is secreted by the pancreas (pancreas) and attaches to the cell wall and carries sugar from the blood into the cell and to take advantage of it. As for polycystic ovaries, it is unable to do what was previously mentioned, which stimulates the pancreas to continue excreting it, which raises its blood level.
This affects the ovaries in disturbing their response to hormonal signals from the brain that stimulate the growth of eggs, causing the growth of eggs to stop early. It also affects the increased secretion of male hormone from the ovaries and the increase in the response of body cells to it.
Diagnosis: not difficult.
1- Symptoms
2- Laboratory tests
- LH elevation in relation to FSH is the most important
- High insulin, although blood sugar is normal
- High male hormone testosterone
- Milk hormone increases for some only
- High female hormones E1, E2
- Decreased receptors for sex hormones
- Sometimes thyroid hormones are disturbed
3- Abdominal or vaginal ultrasound examination, and vaginal examination is preferred for its high accuracy, unlike abdominal ultrasound examination (error is high).
treatment
The disease cannot be cured, but the symptoms that bother the patient the most can be treated.
The most important treatment is to lose weight with food and exercise.
1- Menstrual disorder: the contraceptive pill or progesterone pills and metformin pills at a dose suitable for weight.
2- Coarse hair: anti-male hormone pills for a period of no less than 6-9 months and the symptoms return as soon as the pills are stopped and they have side effects with prolonged use. Therefore, we recommend other methods of hair removal, especially laser.
3- Weight gain: according to the severity of the disease. Both things lead to each other, as weight gain is associated with hormonal disruption, and this leads to cyst and vice versa, as hormonal disorders can be the cause of weight gain. Therefore, we recommend diet and exercise programs for weight loss.
4- Infertility:
- Drug treatment:
- Metformin pills, which help regularize hormones, reduce the severity of the disease, increase the ovaries' response to stimulant treatments, reduce the risk of ovarian irritation when stimulated with medication, and reduce the abortion of pregnancy in the first trimester of pregnancy. It should be continued for at least 3 months and during the months at the beginning of pregnancy.
- Ovulation induction drugs, either in the form of pills or needles, require monitoring the ovaries and determining ovulation days and dates for the sexual marital relationship, and this makes the pregnancy rate almost double the normal rate.
- Surgical treatment:
- With laparoscopic ovarian perforation, the success rate is high.
Long-term complications of a cyst
1- Diabetes: it is preferred to regularly check blood sugar. 2- Cancer of the lining (cavity) of the uterus: it is preferred to periodically check the thickness and shape of the endometrium. 3- High blood pressure: it is preferred to regularly measure blood pressure. 4- Fat increase: it is preferable to measure it periodically and treat it because it may cause some cardiovascular disease.
Dr. Abdel Raouf Riad