Contents
Thumb tendinitis
Thumb tendinitis is known as De Quervain's Tendinosis, and the thumb tendon is the cord that muscles use to stretch and move the bones of the hand. And the thumb tendon becomes inflamed due to the narrowing of the canal in which the thumb tendons pass, or because the tendons occupy a larger area of ??the canal, and as a result, the victim may suffer from pain when moving the hand or thumb or when rotating the wrist or grasping things with the cuff of the hand forcefully. [1]
Causes and risk factors for thumb tendinitis
The frequent use of the wrist is the most common cause of thumb tendinitis, and by frequent use we mean frequent and daily movements that can cause irritation and pain. Examples of such movements include lifting a child into a car seat and lifting heavy shopping bags with a hand grip. There are a group of factors that may increase the risk of developing thumb tendinitis, including the following: [2]
- Gender: Women are more likely to have thumb tendinitis than men.
- Age: The chance of developing thumb tendinitis increases after you reach forty.
- Hobbies or work: Some hobbies or work that involve moving the hand and wrist frequently can cause inflammation in the thumb tendon.
- Bruising: Bruising on the hand can cause scar tissue to form, which may restrict tendon movement.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy may cause thumb tendinitis.
Symptoms of thumb tendinitis
Thumb tendinitis causes many symptoms, and some of them are listed below: [3]
- Feeling pain in the wrist on the thumb side, which is the main and distinctive sign of thumb tendinitis, and what distinguishes this pain is that it may appear gradually or suddenly, and it may extend to the top of the forearm.
- Swelling and swelling of the wrist side of the thumb side, and in some cases the swelling may be accompanied by the emergence of a fluid-filled sac in this area.
- Difficulty moving the thumb and wrist due to pain and swelling.
Thumb tendinitis treatment
The treatment for thumb tendinitis aims to reduce the symptoms of the inflammation, allow normal movement of the thumb without any restriction, and also prevent the return of the injury. It is worth noting that symptoms require 4-6 weeks to improve if treatment is started early, and in the case of thumb tendinitis during pregnancy, symptoms often disappear towards the end of pregnancy or lactation. [4] The following is a list of some of the methods used in treating thumb tendinitis:
Home remedies
Some home measures can improve symptoms of thumb tendinitis, including: [5]
- Wearing the splint to restrict the movement of the thumb and wrist in order to give the tendons a chance to heal and recover. The splint is worn throughout the day, without removing it for a period of 4-6 weeks.
- Avoid thumb movements that can cause pain whenever possible.
- Putting ice on the affected area.
Medicines treatment
Tendinitis can be treated with medications that reduce inflammation or pain. Examples of these medications include: [4]
- Pain killers: can be used for some types of pain - killing drugs that do not require a prescription for dispensing, Examples include Ibupoprofen and Naproxen.
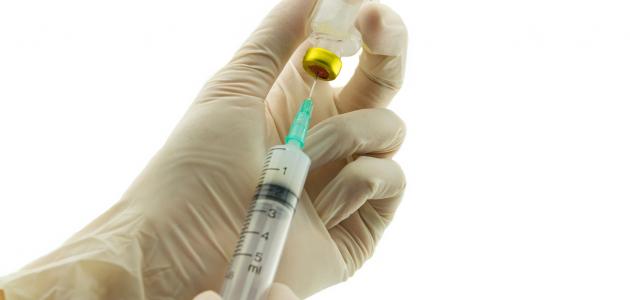
- Corticosteroids: These drugs are used in the form of injections administered into the tendon sheath to reduce swelling and swelling. It is worth noting that using these drugs early during the first six months of treatment helps to get rid of symptoms completely, as many patients recover after taking one injection of treatment.
natural therapy
Exercises help treat thumb tendinitis, and the following are some simple exercises that a sufferer can adhere to to help with treatment: [6]
- The first exercise: This exercise can be done by spreading the affected hand on a flat surface such as a table, and gently moving the injured thumb away from the table with the other hand, and then returning it again slowly and smoothly, and this movement should be repeated 5-10 times.
- The second exercise: This exercise can be done by spreading the affected palm flat on a table, and moving the thumb sideways while keeping it touching the table surface and returning it to its place again, and the exercise is repeated 5-10 times.
- The third exercise: You can complete this exercise by placing an elastic band around the fingers and thumb and moving the thumb so that it resists the rubber band, for ten times.
- The fourth exercise: This exercise is done by placing the affected hand on a table with the palm of the palm facing upward, and bringing the thumb closer to the little finger in an attempt to touch it, and maintaining this position for six seconds, and this exercise should be repeated ten times.
- The fifth exercise: This exercise is done by placing the affected arm against the injured person, with the palm of the hand up, and bending the palm from the wrist with the other hand for 15-30 seconds, and this exercise should be repeated three times.
- The sixth exercise: This exercise is performed by pressing a rubber ball for 5 seconds and then opening the fist. The exercise is repeated 15 times with the aim of strengthening the hand grip .
Surgical treatment
Doctors resort to surgical treatment after previous treatment methods failed to relieve symptoms associated with thumb tendinitis and solve the problem, and surgery can be performed in the doctor’s office without the need to sleep in the hospital, and during the surgery a small incision is made in the canal in which the thumb tendons pass to expand it and facilitate movement Tendons. After the operation, the patient needs to do some physical therapy exercises to prevent tendinitis again. [4] [5]
References
- ? "DE QUERVAIN'S TENOSYNOVITIS" , www.assh.org , Retrieved 28-6-2018 . Edited.
- ? “De Quervain's Tenosynovitis” , /familydoctor.org , Retrieved 28-6-2018 . Edited.
- ? "De Quervain's Tendinosis" , orthoinfo.aaos.org , Retrieved 28-6-2018 . Edited.
- ^ A b v "DE QUERVAIN'S TENOSYNOVITIS" , Www.mayoclinic.org , Retrieved 28-6-2018. Edited.
- ^ A b "? What ' 's De Quervain's Tenosynovitis" , the www.webmd.com , Retrieved 28-6-2018. Edited.
- ? "? What is De Quervain's tenosynovitis" , www.medicalnewstoday.com , Retrieved 6/28-2018. Edited.