Contents
- 1 Loss of consciousness
- 2 Causes of loss of consciousness
- 3 factors increase the risk of fainting
- 4 symptoms and signs of loss of consciousness
- 5 types of loss of consciousness
- 6 How to deal with cases of loss of consciousness
- 7 Diagnosis of loss of consciousness
- 8 Treatment of loss of consciousness
- 9 References
Unconsciousness
People often mean temporary loss of consciousness when they talk about loss of consciousness, and that temporary loss of consciousness is also known as syncope, and its occurrence is due to poor blood flow to the brain, and in fact fainting occurs as a natural response of the body to stay alive When there is a significant drop in the amount of blood and oxygen reaching the brain, the brain responds by stopping the work of all non-vital organs until the blood flow to the vital organs is concentrated. The loss of consciousness is not considered a serious health problem in most cases, but it may It is evidence of a serious health problem in some cases, so all cases of fainting must be dealt with as a health emergency until the cause that led to the occurrence of the coma is determined and the symptoms associated with it disappear. [1] [2]
Causes of loss of consciousness
There are many causes and factors that lead to loss of consciousness, including the following: [3] [4]
- Sudden drop in blood pressure .
- arrhythmia.
- Standing for long periods of time.
- Exposure to severe pain.
- Extreme fear.
- Pregnancy.
- Dehydration .
- Fatigue and exhaustion
- Seeing blood.
- Exposure to psychological or emotional trauma .
- Low blood sugar.
- Severe coughing
- Exposure to seizures.
- Taking illegal drugs and medicines.
- Drinking alcohol.
Factors that increase the risk of fainting
People with the following health conditions have an increased risk of losing consciousness: [3]
- Disease diabetes .
- Heart disease.
- Hardening of the arteries .
- Arrhythmia.
- Anxiety disorder and panic attacks.
- Chronic lung diseases such as emphysema.
Symptoms and signs of loss of consciousness
A number of symptoms and signs may precede the occurrence of coma, including the following: [4]
- Feeling sick.
- Blurred speech.
- A sudden change in body temperature .
- Sudden sweating.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Vision disturbance.
- Feeling lightheaded and dizzy .
- Feeling numb.
- Accelerated heart rate .
Types of loss of consciousness
There are many different types of syncope, and the following three are the most common. They are listed below: [3]
- Fainting vascular vagal: and adopts this kind of fainting to stimulate the vagus nerve through exposure to emotional trauma, or because of the vision of the blood, or as a result of prolonged standing.
- Carotid sinus syncope: This type of fainting occurs when the carotid artery in the neck is subjected to pressure, due to a change in the position of the head, or due to wearing a narrow collar on the neck.
- Fainting Situational: occurs this type of fainting due to pressure during urination, or output, or cough, or because of a health - related problems in the digestive system.
How to deal with cases of loss of consciousness
There are some measures that must be taken if a person feels the possibility of fainting, including: [1]
- Find a suitable place to sit or lie down.
- Place the head between the knees after sitting.
- Getting up slowly after feeling better.
There are also some procedures that can be followed to deal with unconscious people, including the following: [1]
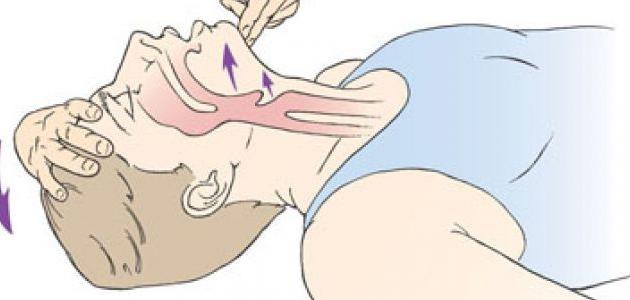
- Extend the patient on his back.
- Raise the patient's feet about 30 cm from the level of the heart to increase the amount of blood flowing towards the brain.
- Try to relieve stress by removing necklaces, belts, ties, and tight clothing.
- Preventing the person from getting up immediately after regaining consciousness.
- Call 911 and seek medical help if the person does not regain consciousness after one minute.
- Ensure that there is nothing obstructing the respiratory tract in the event that the person's breathing stops, and in the event that the person does not regain his ability to breathe normally, cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) must be performed until the person regains his ability to breathe or Until medical help arrives.
Diagnosis of loss of consciousness
The cause of unconsciousness is diagnosed through a number of different tests, including the following: [3]
- Clinical examination, by asking the patient about the circumstances during which the fainting occurred, and the person's medical history, including the medications that they are taking, whether they are prescribed or over the counter medications.
- An electrocardiogram .
- An ECG using a Holter monitor, a portable device that is worn for at least a full day, during which the electrical activity of the heart is recorded.
- Echocardiogram, in which the heart is imaged using sound waves.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG) to detect the electrical activity of the brain.
Treatment of loss of consciousness
If the coma is linked to another health condition, this condition must be treated to avoid a recurrence of the coma in the future, and if the coma occurs without a health problem, then the affected person often does not need to undergo any kind of treatment, and to avoid the coma occurring again, the person should Avoid exposure to some factors that increase the chance of fainting, such as standing for long periods, being dehydrated, and so on, as mentioned above. (English: β-Blockers) in some cases where the cause of fainting is related to the cardiovascular system to avoid the occurrence of coma in the future. [1]
References
- ^ A b T w Christian Nordqvist (1-12-2017), "What ' Fainting Is And What Causes It?" , Www.medicalnewstoday.com , Retrieved 28-3-2018. Edited.
- ↑ Jerry R. Balentine, "Fainting" , www.emedicinehealth.com , Retrieved 28-3-2018. Edited.
- ^ A b t w "What Causes Fainting?" , www.healthline.com , Retrieved 28-3-2018. Edited.
- ^ A b Corey Whelan, "What ' To And of After During of the Expect of a Syncopal Episode" , Www.healthline.com , Retrieved 28-3-2018. Edited.