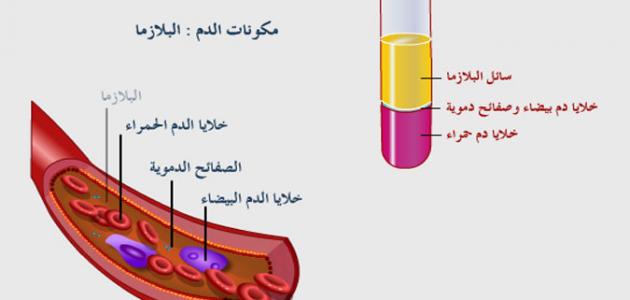
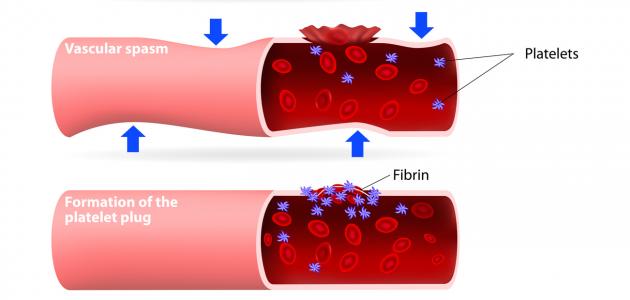
When there are wounds or bruises in the arteries, the blood vessels quickly constrict until the bleeding stops, and there are some small cells called platelets that work to form a barrier to close the wound or bruise in the affected blood vessels, and many proteins that are related to healing are activated, and they produce fibers that work These platelets are strengthened, and blood clumps are formed that stop the continuous bleeding in the injured blood vessel, and at the same time the vessel is rebuilt again and the damaged cells are replaced by healthy cells and the clumps begin to disappear. In general, the wound healing processes are somewhat complicated and take place with many elements that work on blood clotting in the human body.
Contents
Types of blood thinners
- Classical type A blood thinners arising from deficiency of clotting component number eight and is very common.
- Type B blood fluidity, which is widespread in the Arab world, which arises from a lack of clotting component number nine.
- Type C blood thinners, which arise from a deficiency of clotting element number eleven, which is the least common type.
Causes of blood thinning disease
- A genetic disorder responsible for the manufacture and production of clotting elements in the blood, whether these genes are inherited through the father or the mother.
- The genetic mutation that occurs when the elements of clotting are formed in a person, even if there is no infection in the mother or father.
Symptoms of infection in blood thinning disease
- Exposure to severe bleeding in any organ of the body.
- Bleeding can be internal or external, especially in the joints and muscles.
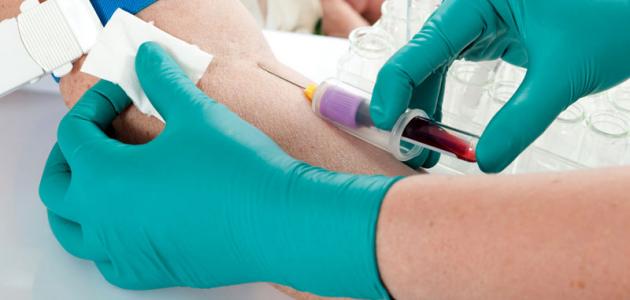
- Bleeding occurs after simple operations such as: cleansing, extraction of a tooth, giving an injection during the treatment period, or taking blood samples.
- Among the dangerous types of bleeding are: Brain hemorrhage, whose symptoms are: convulsion and coma; Healing a wound depends on the age, activity and movements of the injured person.
- When the child begins to walk with his first steps, he may fall repeatedly and suffer bruises and wounds and severe bleeding in the joints of the extremities, especially in the knees, and the appearance of fibers and severe stiffness in the joints due to severe bleeding.
- General muscle weakness, which is caused by inflammation in the bleeding stages, and after a short period of time, the child may become disabled, and in puberty he may need operations in which the joints are changed.
Treating blood thinners
- To stop the bleeding, ice can be used to relieve, but not to fundamentally solve the problem.
- Taking a pain reliever that contains a clotting protein, and this reliever can be given to children.
- Giving or injecting a sick child every forty-eight hours with clotting agents; It is better than any treatment because it preserves the joints and muscles, and there can be no obstruction in the future.
- Plasma therapy.
- It is genetically treated once every whole year, thus the person avoids the disease being transmitted by heredity in the future.