Contents
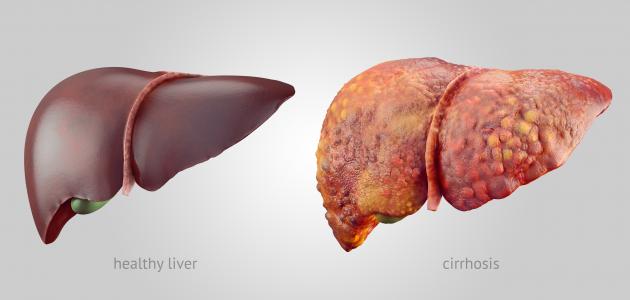
Hepatic disease
Known epidemic disease hepatitis, or liver disease epidemic, or hepatitis C, or viral hepatitis as an infection of the tissues of the liver , causing inflammation and swell, and damaged, and their occurrence is due to viruses different; Including hepatitis C viruses (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E), [1] and in some cases hepatitis may be attributed to other types of viruses; Such as cytomegalovirus, Episten Bar virus, and Herpes simplex virus, [2]Hepatitis can be classified into two main types: These are acute hepatitis, which lasts for less than six months, and chronic hepatitis, which lasts for more than six months, and may be for life unless treated. [3]
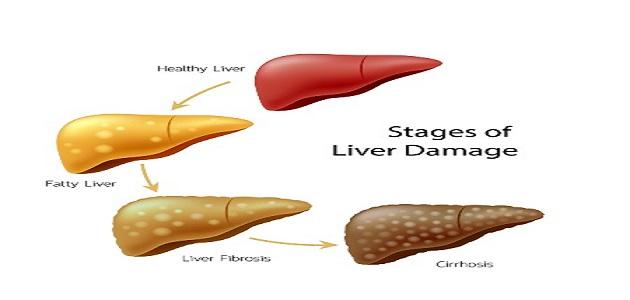
In general, most people recover from hepatitis C infection, but this condition may harm other body organs, especially if the appropriate treatment is not received, as it may cause liver tissue destruction, liver failure, weakening of immunity, and it may develop into liver cancer in some cases, and moreover, hepatitis C disease may spread easily between people. Nevertheless, prevention of the disease is possible and can be achieved by taking measures that will be explained later in this article, [1] [2] and according to For a study published in the "World Journal of Clinical Cases" in 2018, the total number of people infected with one or more liver viruses is approximately 2.3 billion people around the world. [4]
Types of hepatotoxic disease
As we mentioned earlier that there are five main types of hepatitis viruses, and although they all cause hepatitis, there are differences between them, and they can be explained as follows: [5] [6]
- Viral hepatitis A: Hepatitis A, short for (HAV), infection of this type is transmitted through the stool. A few weeks in mild cases, to several months in severe cases.
- Viral hepatitis B: , and Acronym (HBV), and moves this kind of healthy person to infected through blood or semen, or other body fluids, may occur through several ways; These include sexual intercourse, sharing needles and other injection equipment, or from mother to child during childbirth.
- Viral hepatitis (c): , and Acronym (HCV), and travels through the blood primarily; Through blood transfusions and the use of syringes contaminated with the virus during medical procedures or drug use, it can be transmitted through sexual contact, but it is less common compared to blood.
- Viral hepatitis (d): , and Acronym (HDV), and limited transmission between people with rheumatoid hepatitis C; That is, it does not transmit from infected to normal from the hepatic epidemic, and it should be noted that infection with hepatitis B types (B) and (D) at the same time increases the severity of the situation and worsens the complications resulting from that.
- Hepatitis E: , abbreviation (HEV), and is the most common cause of outbreaks of hepatitis C in developing countries, and it has become an important cause of hepatitis C in developed countries, where this virus is transmitted through food. , Drink, and water contaminated with the virus.
To learn more about the methods of transmission of hepatitis disease, you can read the following article: ( Methods of transmission of the hepatitis virus ) .
To learn more about hepatitis B, read the following article: ( Hepatitis B ) .
To learn more about hepatitis C, read the following article: ( Hepatitis C ) .
Symptoms of hepatic disease
Many people may not be aware of their infection with hepatitis C due to the absence of symptoms that infer their infection with the disease, and if they do appear, this usually occurs after exposure to a period ranging between two weeks to six months in cases of acute hepatitis C, and after decades in cases Chronic hepatitis C infection, [7] As for the nature of the symptoms of hepatitis C disease that may appear in an advanced stage of the disease, we mention the following: [8]
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite .
- High body temperature.
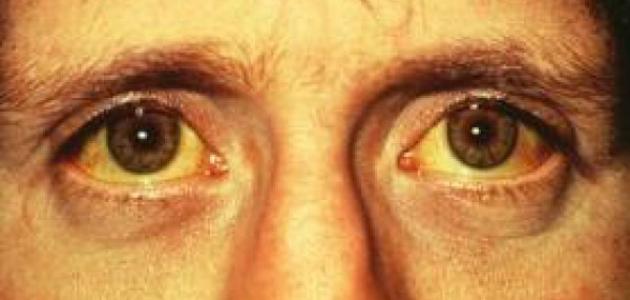
- Jaundice ; Which means yellowing of the skin and the white area of the eyes.
- Fatigue.
- stomach pain.
- Forgetfulness .
- Mood swings.
- Dark-colored urine.
- Intestinal bleeding ; This can be inferred by observing the stool, which may appear black in the event of intestinal bleeding.
To learn more about the symptoms of hepatitis C disease, you can read the following article: ( Symptoms of hepatitis C disease ) .
Diagnosis of hepatotoxic disease
Hepatitis C disease can be diagnosed in the vast majority of cases using simple blood tests easily and conveniently. As for a liver biopsy, it is one of the procedures that can be used in cases that are difficult to diagnose or if a treatment decision needs to be made based on the severity of the scarring of the liver. , [3] With reference to the simple tests used to diagnose hepatitis C disease, they include the following: [9]
- Blood tests, and the following is a statement of the most prominent:
- Liver Function tests, which detect levels of bilirubin and liver enzymes; Specifically, Aspartate Transaminase (AST), and Alanine Transaminase (ALT) for short.
- Blood clotting tests ; One of them is the measurement of prothrombin time.
- Renal Functions tests.
- Test to measure blood sugar .
- A serology test, which aims to detect IgM antibodies that appear early in acute hepatitis C infection, and IgG antibodies that appear at a later time. From infection.
- Urine bilirubin test.
To learn more about the diagnosis of hepatic epidemic disease, you can read the following article: ( Hepatitis Diagnosis ) .
Treatment of hepatic disease
The treatment of hepatitis C varies according to the virus that causes the condition, and this can be explained as follows: [10] [11]
- Hepatitis A: The treatment plan for this type of infection is to drink large quantities of fluids, eat healthy food , get rest, refrain from drinking alcohol or using drugs that may harm the liver, and avoid strenuous exercise until the acute inflammation period ends; This plan comes from the idea that this type of inflammation always goes away on its own and does not need drug treatment.
- Hepatitis B: as is the case with type A; The treatment plan for viral hepatitis B includes rest, healthy nutrition, and drinking plenty of fluids, as these measures are important in cases of acute inflammation to enable the body to deal with infection, and it is indicated that the acute type disappears on its own without the need for a medical procedure. As for the more severe cases, they may need anti-viral treatments or a hospital stay to avoid complications, [12] and treatment for chronic hepatitis B is long-term and possibly life-long in order to avoid transmitting the infection to others, and to reduce the risk of other liver diseases, and treatment includes the following: : [13]
- Antiviral drugs, which are taken under the supervision of a doctor with the aim of fighting the virus and slowing its ability to damage the liver, and the oral types: Entecavir, Tenofovir, Adefovir, and Telbivudine. And lamivudine .
- Injection of interferon ; It is used mainly for young people with hepatitis B who do not want long-term treatments, or women who want to become pregnant within a few years after completing the course of treatment, with attention to the inability to use interferon injections during pregnancy.
- Liver Transplant ; This option can be used if the liver has been severely damaged.
- Hepatitis C: The available treatment is limited to the chronic type only, and despite the availability of many drugs used in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C, they are no longer of use at the present time as a result of the disease progression, and they are replaced by other drugs that are given Under the supervision of a doctor, and the most appropriate ones are selected depending on several factors. Among them is the medical history of the injured person. Including having other liver diseases or human immunodeficiency virus , previous treatments and results of their use, interactions and drug allergies are also taken into consideration .And the genotype, whether the person had previously undergone a liver transplant or not, and about the drug options available in this case, they are taken in different groups, and no specific drug is given alone, and include interferon injections, and certain types of oral drugs; Such as ribavirin, elbasvir, grazoprevir, and ledipasvir. [14] [11]
- Hepatitis D: This type is treated by giving the patient the drug pegylated interferon alpha for at least 48 hours, regardless of the type of response while receiving this treatment, and in cases of fulminant hepatitis (*) Or the final stages of liver disease, and a person may be subjected to a liver transplant. [15]
- Hepatitis E: As is the case with types (A) and (B); The treatment plan for acute hepatitis E also includes rest, healthy nutrition, drinking plenty of fluids, and abstaining from alcohol, and certain types of medicines may be used. Cala-ribavirin or the medicine peginterferon alpha-2 (a), and the patient should not use any types of medicines, vitamins, nutritional supplements, or herbal prescriptions without consulting a doctor, because some of them have a harmful effect on the liver, and it is advised to review the doctor periodically until The patient's full recovery is ensured. [16]
To learn more about the treatment of hepatitis, you can read the following article: ( Treatment of viral hepatitis ) .
Prevention of hepatic disease
The risk of developing hepatitis can be reduced by following all preventive advice, among which we mention the following: [17]
- Obtaining vaccinations to prevent the risk of infection with hepatitis A and B, and this concerns people in general, and in particular those who have risk factors for developing hepatitis C, those who suffer from other health problems, and health care workers Or public safety , as for type (C) of the hepatitis virus, it does not have a vaccine, and a doctor can be consulted to assess the need to obtain these vaccines.
- Wash hands thoroughly after using the bathroom or changing diapers, and they must be washed thoroughly before preparing or eating food.
- Avoid illegal sexual relations to reduce the risk of contracting an STD ; These include hepatitis C, which is transmitted through menstrual blood, vaginal fluids, and semen.
- Avoid sharing needles and syringes with others.
- Alone with personal items that may be stained with blood; Such as a razor blade, nail clipper, blood glucose meter, or toothbrush, and not allowing others to use it, as well as not using their personal items.
- Wear protective gloves if handling another person's blood is necessary.
- Adhere to general safety principles and follow infection control methods and safe injection practices.
To learn more about the prevention of hepatotoxic disease, you can read the following article: ( Prevention of Hepatitis C ) .
Margins:
(*) Fatal hepatitis: a clinical syndrome characterized by severe impairment of liver function, which leads to a coma in the liver, and a decrease in the productive capacity of the liver, and this condition develops within eight weeks of the onset of hepatitis. [18]
References
- ^ A b "What Is Viral Hepatitis?" , www.niddk.nih.gov , May 2017, Retrieved 4/4/2020. Edited.
- ^ A b "Viral Hepatitis" , Www.my.clevelandclinic.org , Retrieved 4/4/2020. Edited.
- ^ A b "Hepatitis (Hepatitis A, B, And the C)" , Www.gi.org , Retrieved 4/4/2020. Edited.
- ↑ World J Clin Cases (2018 Nov 6.), "Update on global epidemiology of viral hepatitis and preventive strategies" , www.nb.nlm.nih.gov , Retrieved 4/4/2020. Edited.
- ↑ "What is hepatitis?" , www.who.int , September 2019, Retrieved 4/4/2020. Edited.
- ↑ "VIRAL HEPATITIS" , www.vdh.virginia.gov , October 18, 2019, Retrieved 4/4/2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Viral Hepatitis" , www.cdc.gov , February 13, 2020, Retrieved 4/4/2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Viral Hepatitis Signs and Symptoms" , www.ucsfhealth.org , Retrieved 4/4/2020. Edited.
- ↑ Dr Nick Turnbull, Dermatology registrar, Auckland and Greenlane Hospital, Auckland, (2010), “Viral hepatitis” , www.dermnetnz.org , Retrieved 4/4/2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Types of Viral Hepatitis" , www.drugabuse.gov , Retrieved 4/4/2020. Edited.
- ^ A b the Charles , Patrick Davis , , MD, : PhD (1/31/2020), "A Guide , the Picture To Hepatitis" , Www.emedicinehealth.com , Retrieved 4/4/2020. Edited.
- ^ "Hepatitis B" , www.mayoclinic.org , Oct. 27, 2017, Retrieved 4/4/2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Hepatitis B" , www.drugs.com , Oct 17, 2019, Retrieved 4/4/2020. Edited.
- ↑ Michael W. Smith, MD (August 23, 2019), "Hepatitis C and the Hep C Virus" , www.webmd.com , Retrieved 4/4/2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Hepatitis D" , www.who.int , Retrieved 19-04-2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Hepatitis E" , www.niddk.nih.gov , Retrieved 19-04-2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Viral hepatitis" , www.womenshealth.gov , Retrieved 4/4/2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Fulminant Hepatitis B" , pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov , Retrieved April 24-2020 . Edited.