Contents
Rough knee disease
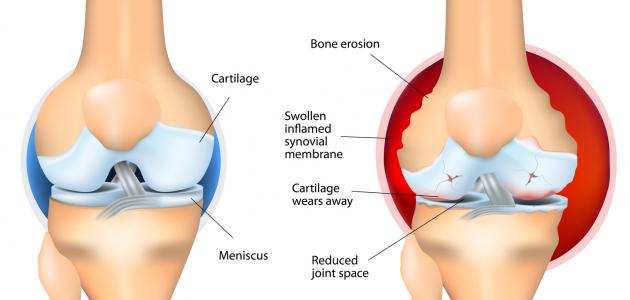
This disease is also known as "erosive arthritis" or "friction of joints" in the knee in which the cartilage in the joint dissolves due to the friction of the two bones with each other, so the cartilage is no longer able to absorb the pressure on it, and this causes pain, swelling, and a decrease in the range Movement for the knee. This type of disease occurs specifically with people over the age of 45 years, and it can occur with young people as well, and women are more susceptible to the disease than men. [1]
Stages of knee roughness
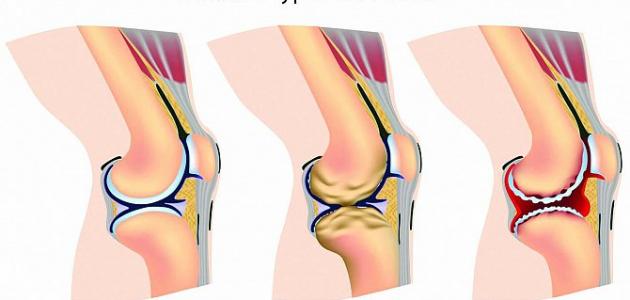
Rough knee disease passes through several stages, namely: [2]
Phase zero
Stage 0 is the stage when knee health is normal, where the knee joint is without any signs of pain or swelling.
The first stage
At this stage, a protrusion appears in the bones , but the person will not experience any pain or discomfort, and this stage can develop when the bones meet each other.
The second phase
This stage is also considered to have a mild impact. Where the cartilage is in a healthy size, that is, the space between the bones is normal, and the synovial fluid is still present, but the x-ray may show more bump in the bones from the first stage, and the person will suffer from pain symptoms after a long day of walking or running, and he will feel more stiff In the joint if it has not been moved for hours.
third level
In this stage the cartilage dissolves clearly, and the space between the bones is shortened, and the person suffers in this stage from frequent pain when walking and running, bending, and kneeling, and the joint becomes more rigid after sitting for long periods of time or upon waking up in the morning, and joint swelling may occur After long periods of movement.
The fourth stage
This stage is considered the most difficult stage of the disease, as the cartilage degrades greatly, and the distance decreases to the point of friction with the bones, and the person then suffers from great pain and lack of comfort when walking.
Symptoms of knee roughness
Among the symptoms of knee roughness are: [3]
- Feeling of gradually increasing pain in the knee.
- Suffering from knee irritation often resulting from the formation of bone growths.
- Knee swelling and swelling, in addition to redness and high temperature of the skin covering it.
- Frequently injured by twisting and stiffening of the knee.
- Hear popping sounds from the knee.
- The knee range of motion becomes less.
- The appearance of deformities in the external shape of the knee.
Rough knee causes:
- High weight is the most important factor in osteoarthritis, especially for women.
- Eating legumes and meat in an exaggerated manner, through which uric acid increases, causing knee roughness.
- If the legs are bent, they overload the joint and certain parts of it.
- Genetics also There are studies that have shown that the presence of genetic factors plays a contributing role to osteoarthritis.
- Exposure of the knee to any injury such as fractures, cutting the meniscus or ligaments.
- The incidence of knee roughness increases in women in particular than men, after the age of fifty.
- When the knee is exposed to frequent fatigue and stress, such as when the person takes the form of squatting in his sitting for a long time, and also the frequent climbing and descending of stairs, and violent sports.
- When the joint is exposed to cold air
- Standing for a long time, and not being careful to exercise.
Some of the guidelines for treating knee roughness:
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet that contains low levels of uric acid.
- Taking ginger, as it works to treat arthritis.
- In the event of climbing the stairs and in order to be careful to avoid feeling pain, lean on his wall, and go up step by step using the uninjured leg first.
- Work to get rid of weight, by increasing the intake of vegetables and fruits and reducing fats and starches, in addition to exercise.
References
- ↑ “Osteoarthritis of the Knee (Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee)" , www.webmd.com , Retrieved 10-29-2017. Edited.
- ↑ Kimberly Holland (4-1-2017), "Stages of Osteoarthritis of the Knee" , www.healthline.com , Retrieved 29-10-2017. Edited.
- ↑ "7 Symptoms of Arthritis in The Knee" , www.healthline.com , Retrieved 29-10-2017. Edited.