Contents
What is sputum
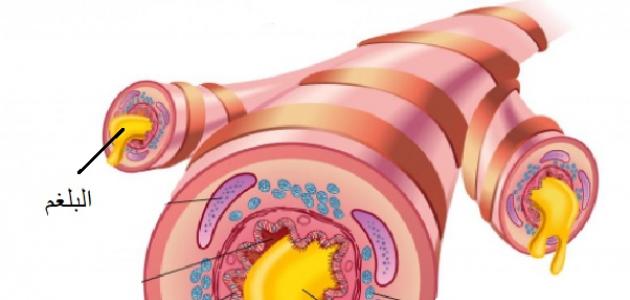
Sputum is a sticky and dense substance consisting mainly of mucus, and it may also contain dead cells, pus, and foreign particles, and in the normal position mucus is produced from the throat, lungs and bronchial passages, in order to maintain the moisture of the delicate tissues that make up the passages Airways, and the importance of moisturizing the airways is enabling them to adhere to foreign substances that may enter them, after sticking to them they get rid of them to the outside, but in some cases the secretion of this mucus increases, and this usually occurs after exposure to the lungs of damage as is the case when they are infected with infection Or, as a result of exposure to dust or smoke, etc., regardless of the reason, the increase in mucus in the airways creates a sticky substance known as phlegm, and this substance must be expelled from the body by coughing to keep the airways clean. [1] [2]
Causes of phlegm
There are many causes that may lead to sputum formation, and vary in severity. The following are the most common causes of sputum : [3]
- Smoking: phlegm accumulates in the smoker's lungs, causing a cough, and the color of the phlegm is green, yellow, or blood-colored.
- Asthma: , in which the airways of the affected person are sensitive and are overly affected by environmental pollution, respiratory infections, and allergens in general, which in turn lead to inflammation of the airways and increased sputum production.
- Cystic fibrosis: It is a genetic disease that occurs due to a mutation in an important gene in the body, and leads to blockage of the small airways due to the production of very thick mucus, which in turn causes difficulties in the ability to breathe, and thick mucus is a fertile ground for growth Bacteria, and this leads to a chronic bacterial infection in the lungs.
- Tract infection Respiratory: and Acronym (RTI), may indicate the secretion of sputum which is different from the color of saliva on the presence of tract infection lower respiratory tract , and generally be the color of phlegm in the early stages of green infection dark, becomes lighter gradually with improved infection And, in some cases, the color of the sputum may be yellow, gray or rust colored, and when a bacterial infection occurs in the respiratory system, the phlegm has a foul odor and dense texture, and among the most prominent respiratory infections are the following: [1]
- Acute bronchitis or acute bronchitis.
- The common cold, which is a viral infection that affects the respiratory system.
- Croup is an infection caused by a viral infection in the larynx and windpipe.
- Inflammation of the epiglottis , a rare inflammation dangerous in the epiglottis, knowing that the epiglottis is an extension of cartilage covers the trachea to prevent inhalation of food during the process of swallowing, inflammation and affects mainly infants and children.
- Influenza , also called influenza.
- Laryngitis (Laryngitis).
- Pneumonia , also called pneumonia.
- Sinusitis.
- Sore throat, or pharyngitis.
- Tonsillitis, which may be caused by streptococcal bacteria.
- Tuberculosis or TB , a contagious disease that affects the lungs.
Sputum risk factors
There are some factors that increase the chance of sputum formation, and they are known as risk factors, including the following: [4]
- Being in a dry environment, this may be due to the use of air conditioning or heating equipment.
- Not drinking enough water, or drinking too much of drinks that may lead to a loss of fluids from the body, such as: coffee, tea and alcohol.
- The wrong use of drugs that cause dehydration, and thus lead to increased phlegm density, such as: antihistamines , and decongestants .
Signs and symptoms accompanying the phlegm
Sputum may be accompanied by the emergence of other symptoms, which differ according to the cause, for example, if the sputum is caused by an infection, it may also suffer from fever and body pain, and when sputum is a symptom of a disease or an abnormal state, it takes on certain characteristics, which It includes the following: [1]
- Abnormally thick or bushy, or purulent.
- It might be tinged with blood.
- It is produced in very large quantities.
- A change in the color of the sputum, but this is not usually a cause for concern, and doctors do not rely on it during the diagnosis, but rather reflects the extent of inflammation of the tissues of the respiratory system, and indicates that the immune system is fighting infection. [5]
Diagnostic tests and examinations
It is possible to perform some diagnostic tests that deal with analyzing sputum to determine its components, with the aim of evaluating infection if any, or detecting more serious cases. These tests include the following: [6]
- Sputum culture: It is a medical test to detect bacteria or fungi that may cause infections in the respiratory system, such as pneumonia. Where the sputum sample is placed in the agar plate, which promotes the growth of microbes, and monitors the occurrence of growth, and if no growth occurs, the result of the culture is negative, meaning that the sample is free of germs or microbes, while if a growth occurs in the culture the result is positive, and once the bacterial strain is determined, Other tests may be done to determine the most effective antibiotic for treating an infection, and this is called an antibiotic susceptibility test. . [7]
- Sputum cytology, in which a sputum sample is examined under a microscope, to detect the presence of abnormal cancerous cells, when lung cancer is suspected, and it is also possible to conduct an examination to detect some non-cancerous lung conditions. [8]
- Rapid: sputum tests also called DNA amplification tests, Acronym (NAATs), used to diagnose TB, when other tests show the probability of infection. [9]
Sputum treatment
When a large amount of phlegm is excreted, it is possible to get rid of it either by spitting it out or by swallowing it, and both methods are healthy. When swallowing phlegm, the stomach eliminates the effect of the bacteria and performs its role in getting rid of other waste products in the phlegm. Sputum problem, [10] In general, there are a set of recommendations and tips that help control a phlegm problem (especially if it is chronic): [11]
- Drink more water, and reduce medications or drinks that increase fluid loss from the body as much as possible.
- Use of humidifiers; It helps to moisten the throat and airways and reduce the chance of phlegm.
- Use a saline nasal spray, as it moisturizes the tissues of the nose, throat and nasal passages as well, which contributes to reducing sputum production.
- Ensure that the filters used in air conditioning and heating systems are clean and in good working order, to avoid exposure to dust and other irritants.
Among the drugs that may help get rid of macrophages that are difficult to excrete through coughing are the following: [12]
- Antibiotics: , when sputum is caused by a bacterial infection.
- Expectorants expel sputum by facilitating and stimulating the mechanism of coughing, such as the drug guaifenesin.
- Sputum solvents: , which dissolve the phlegm and reduce its viscosity, such as the drug Acetylcysteine.
References
- ^ A b T. , William C . Lloyd is (2018-12-21), " the Symptoms Sputum" , Www.healthgrades.com , Retrieved 2020-10-20. Edited.
- ↑ Amanda 's Barrell, Jill Seladi-Schulman (2017-8-13), "What ' Can Sputum by tell LANGUAGE?" , Www.medicalnewstoday.com The , Retrieved 2020-10-20. Edited.
- ↑ Amanda 's Barrell, Jill Seladi-Schulman (2017-8-13), "What ' Can Sputum by tell LANGUAGE?" , Www.medicalnewstoday.com The , Retrieved 2020-10-20. Edited.
- ↑ Madeline R. Vann, Sanjai Sinha (9-12-2017), “Everything You Ever Wanted to Know About Phlegm and Mucus , ” www.everydayhealth.com , Retrieved 2020-10-20. Edited.
- ↑ Sharon , Leitch (2020-9-2), "Snot And Sputum" , Www.healthnavigator.org.nz , Retrieved 2020-10-20. Edited.
- ↑ Lynne Eldridge, Doru Paul (2020-5-9), "What Causes the Amount of Sputum to Increase?" , Www.verywellhealth.com , Retrieved 2020-10-20. Edited.
- ↑ Adam Husney, Gregory Thompson, Robert L. Cowie, et al (11-2-2020), “Sputum Culture” , www.peacehealth.org , Retrieved 2020-10-20. Edited.
- ↑ Adam Husney, Gregory Thompson, Robert L. Cowie, et al (2019-6-9), “Sputum Cytology” , myhealth.alberta.ca , Retrieved 2020-10-20. Edited.
- ↑ E. Gregory Thompson, Brian O'Brien, Adam Husney, et al (2020-1-26), “Rapid Sputum Tests for Tuberculosis (TB)” , www.healthlinkbc.ca , Retrieved 2020-10-20. Edited.
- ↑ Laura Tully (2018-12-5), “Mucus and Phlegm: Barometers of Your Health , ” www.premierhealth.com , Retrieved 2020-10-20. Edited.
- ↑ Paul C. Bryson (2018-1-25), “Mucus and Phlegm: What to Do If You Have Too Much” , health.clevelandclinic.org , Retrieved 2020-10-20. Edited.
- ↑ John Carew, Kristin Hayes (2019-12-13), "The Function of Phlegm" , www.verywellhealth.com , Retrieved 2020-10-20. Edited.