Contents
What is urine retention
Urinary restriction is one of the problems that many people, old and young, male and female, suffer from, and it abounds in males over the age of 50 and pregnant women. Urine retention is known as the inability to urinate or completely empty the bladder.
Causes of urine block disease
- Blockage of the urinary tract that coincides with an enlarged prostate, stones, or bacterial infection.
- Imbalances in the nervous system, such as those with diabetes, cerebral strokes, or as a result of a SCI accident.
- Urine retention may be caused by taking some medications.
- It may happen after surgery as a result of anesthesia.
- As a result of urinary tract infections.
Symptoms of urinary retention disease
- Urinary retention disease leads to the inability to urinate, accompanied by an urgent urge to urinate.
- Urinary retention causes pain during urination.
- Urinary retention disease makes urination difficult at the beginning of urination, and the urine comes out light.
- Urinary retention disease leads to the feeling of an urge to urinate immediately after finishing urination.
Diagnosing urine block disease
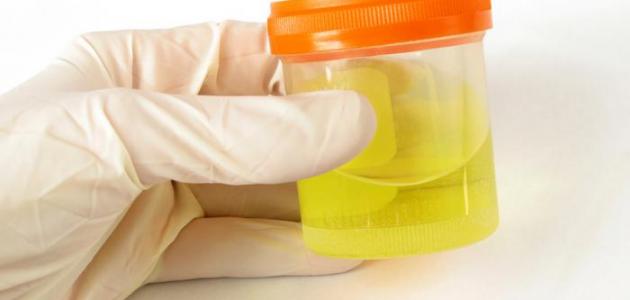
The diagnosis is made through a clinical examination of the patient, where the doctor strikes the tip of his finger in the lower abdomen to know the extent of the expansion of the bladder, and taking a sample of urine and examining it in the laboratory, knowing the amount of urine remaining in the bladder through imaging, prostate examination.
Treatment of urine block disease
- For the prevention and treatment of urine retention, the patient must adhere to complete body hygiene.
- Drink more water as much as possible.
- The use of cabbage juice and a lot of it in the treatment of disease.
- The patient drinks with urine from boiled saffron after a soak.
- Drink onion and watercress juice.
- Maintain as much as possible the level of sugar in patients with diabetes.
- In cases of prostate enlargement, it must be treated immediately.
- Put warm water compresses in the super-pubic area, taking care not to press it.
- In the hospital, nurses must provide a suitable environment and place for urination to the patient.
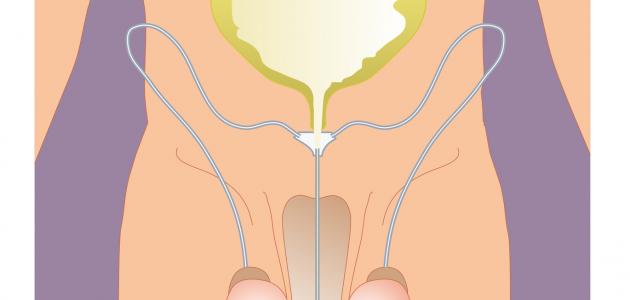
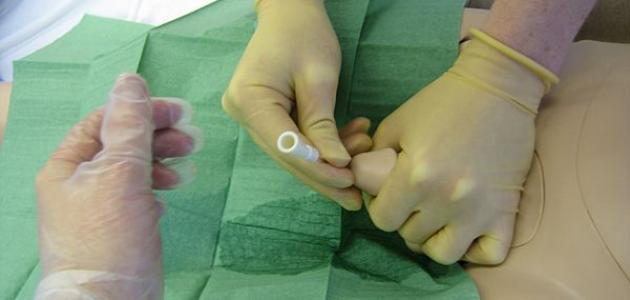
- Using a catheter in the treatment through the urinary tract to open the blockage.
- Giving the patient antibiotics when the cause is a bacterial infection.
- Surgery in chronic cases, especially in the problem of an enlarged prostate.