Contents
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram, electrocardiogram, or electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat [1]. It is a non-invasive and safe procedure and does not pose any risks. A certain pattern, and when there are any differences in the result of the EKG , it may be an indication of a problem with the heart, and doctors often recommend the use of the ECG technique to people at high risk of developing heart disease or for those who exhibit certain symptoms that may indicate Having a heart problem; Like chest pain. [2]
Benefits of ECG
An electrocardiogram is often performed in conjunction with other tests in order to diagnose and monitor conditions that may affect the health of the heart. The following is an indication of the benefits of electrocardiography and what problems it reveals: [2] [3]
- It is recommended for people at high risk of developing heart disease, such as those with a family history of heart disease, those with diabetes , high blood pressure or high cholesterol , people who are overweight, and smokers.
- It is used to screen for symptoms that may indicate a heart problem. Such as chest pain, palpitations, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
- An ECG helps diagnose and detect heart diseases and problems, such as:
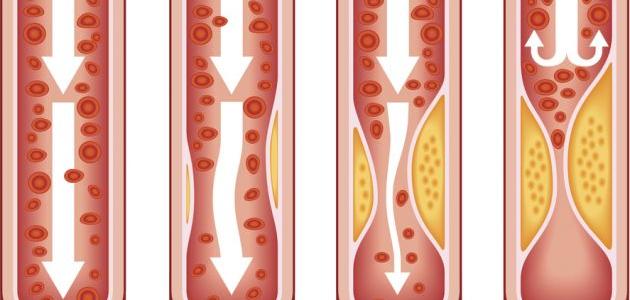
- Coronary Heart Disease Which is accompanied by a blockage or obstruction of blood flow in the heart due to the accumulation of fat in it.
- Arrhythmia; In which the heart beats abnormally. Either too slowly, too quickly, or irregularly.
- Heart attacks ; In it, the blood stops flowing to the heart all of a sudden.
- Cardiomyopathy In it, the walls of the heart become enlarged or thickened.
- It helps in assessing the general health of the heart before undergoing some procedures; Like surgery. [4]
- Helps monitor how the implanted pacemaker is performing. [4]
- It helps determine how well some heart medications are working. [4]
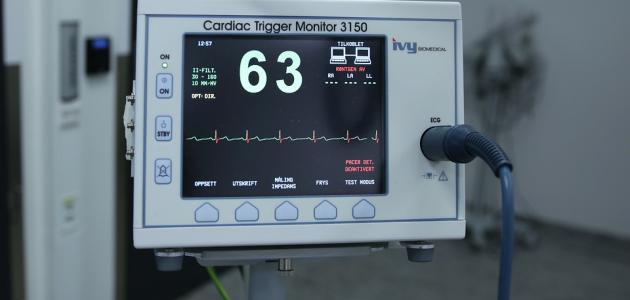
ECG devices
The standard ECG test is the most common measure of the electrical function of the heart, and is most often performed while the patient is lying down, [5] [6] but if symptoms are not persistent such that they come and go and recur and disappear at a later time; These symptoms may not be captured during the recording of the standard ECG, and in this case the doctor may recommend monitoring the electrocardiogram continuously and remotely. There are different types of devices that fulfill this purpose, and some of them are as follows: [7]
- Device Holter: , a small device that can be worn, and works on the recording scheme ECG continuously for a period ranging between 24-48 hours.
- Event Monitor: , which is a portable device that resembles Holter device , but it works on the recording scheme ECG at specific times and for a few minutes each time, so that the button is pressed when feeling the symptoms only, and can some devices make registration automatic when Detecting an abnormal heart rhythm that can be worn for up to 30 days. Therefore, the wearing time is longer compared to the Holter device.
- Stress test: It is called the Stress Test, the Treadmill Test, or the Exercise EKG. In it, the patient walks on a treadmill or rides a stationary bike to monitor the heart during exertion and under stress.
- Heart electroretinogram Average Signal: , a type more detailed electrical diagram heart, which is multi - cardiogram trace over approximately 20 minutes, in order to capture the heartbeat of abnormal that may occur intermittently. [8]
- Exercise test CPR: , and Acronym (CPET), which is used to detect any incidence of heart disease or lung. [8]
How to conduct an electrocardiogram
An ECG will not require any special procedures or examinations as a pre-preparation for planning, and the person who is asked to undergo the test can also eat and drink fluids before the test, [9] and the ECG procedure includes following the following steps: [10]
- Electrodes are attached and adhesive patches are attached to the skin of the arms, chest , and legs, and here the technician may shave the men's chest hair to allow better contact.
- Lying person under examination while the device configures an image of electrical impulses produced by the heart on a graph paper, this ECG is called during rest , and it should be noted that it is possible to be made the same test during the practice of sport .
- The procedure takes about 10 minutes to attach the electrodes and complete the test, but the actual recording of the test only takes a few seconds.
- The results of the examination are read and appropriate action taken accordingly, and the doctor keeps the results of the examination in the file. So that he can compare it with future tests.
How to read an ECG
In fact, it takes months of training and practice to learn and master the EKG reading and to be able to identify these patterns. In general, the ECG report may describe the wave pattern but is unlikely to describe the specific heart condition. This is because the doctor needs to take the medical history into account when determining the possibility of developing a heart condition, and when talking about how to read the ECG, it is indicated that this includes processing the electrical signals generated by the electrodes to obtain the electrical activity of the heart from twelve different angles, as they appear Each angle is a separate track, and the tracking consists of repeating waves that have a certain standard shape, and these waves contain several parts, which are the P wave , the QRS complex, and the ST segment . segment, and T-wave. T wave), and there is also a time interval between the P wave and the QRS complex, called the PR interval, and a time interval between the QRS complex and the T wave, which is called the QT interval , so that changes in length and width are monitored. The height of these waves and the time intervals between them, for example when the QT interval is short; Then this may be a sign of higher levelsCalcium in the blood. [9]
Risks of an ECG procedure
The electrocardiogram (ECG) procedure is safe and cannot result in an electric shock during the test because the electrodes used do not produce electricity, but only record the electrocardiograms of the heart, but some people may feel a feeling of relief and a feeling similar to removing the bandages during the removal of the electrodes, and they may also be injured Some have a slight rash where the patches are applied. [7]
References
- ↑ "Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)" , www.heart.org , Retrieved 5/8/2020. Edited.
- ^ A b " of ECG Test" , Www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au , Retrieved 5/8/2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Electrocardiogram (ECG)" , www.nhs.uk , Retrieved 5/8/2020. Edited.
- ^ A b t "Electrocardiogram" , Www.hopkinsmedicine.org , Retrieved 5/8/2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Electrocardiography" , Stanfordhealthcare.org , Retrieved 5/8/2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Electrocardiography" , emedicine.medscape.com , Retrieved 5/8/2020. Edited.
- ^ A b "Electrocardiogram (Or the EKG of ECG)" , Www.mayoclinic.org , Retrieved 5/8/2020. Edited.
- ^ A b "What Is an Electrocardiogram?" , Stanfordhealthcare.org , Retrieved 9/8/2020. Edited.
- ^ A b "What Is an Electrocardiogram (ECG)?" , www.verywellhealth.com , Retrieved 9/8/2020. Edited.
- ↑ "Heart Disease and Electrocardiograms" , www.webmd.com , Retrieved 9/8/2020. Edited.