Contents
What is a venous thrombosis
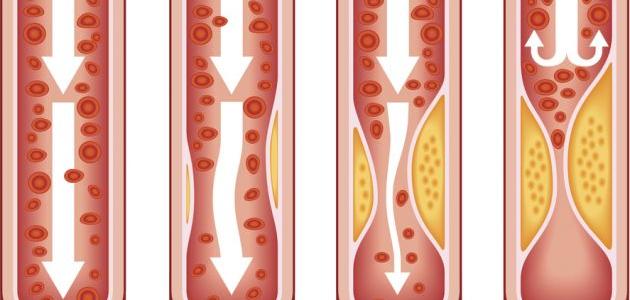
Venous thrombosis is a blood clot in the deep veins located all over the body, and it is more common in the veins of the legs. It results in complete or partial obstruction of the return of blood to the heart. In addition, it leads to death if it reaches the lungs or causes a severe heart attack.
Its causes
Several factors lead to blood clots in the veins, namely:
1) Slow return of blood to the heart, as a result of immobility.
2) Blood accumulation in the veins is caused by:
- a. Immobility.
- B. Miscellaneous medical factors.
- C. Failure of vein valves, especially during pregnancy.
3) vascular edema.
4) Clotting problems that may occur as a result of some diseases or in the elderly.
5) Intravenous implantation of catheter tubes.
Risk factors
The following conditions are prone to deep vein thrombosis, and they are:
1) Heart patients.
2) Pregnant women.
3) Obesity or being overweight.
4) Patients with anemia.
5) Patients with liver disease.
6) Patients with chronic venous failure.
7) Cancer patients.
8) Poisoning of the blood.
9) Patients with intestinal inflammation.
10) Long periods of inactivity and lack of movement and frequent sleep.
11) Complications of sports injuries and fractures.
12) People who are immobile and paralyzed.
13) Take some medications, especially hormonal treatments.
14) Existence of a personal or genetic history of the occurrence of venous thrombosis.
Symptoms of venous thrombosis
1) Red, swollen or painful areas in the legs with a high temperature in the limb. In this case, the patient should not massage or exercise the leg that causes the pain.
2) A feeling of numbness or tingling in the affected part of the body.
3) Feeling of pain in the affected part of the body.
4) A feeling of fever or shivering.
How to prevent blood clotting in deep veins
1) Wearing compression stockings (20-40 mm Hg), as these socks prevent stagnation of the blood that causes a clot.
2) Walk daily and do the necessary exercises for the legs and arms to avoid clotting.
3) Not to sit or lie on one spot for long periods of time.
4) Do not cross the legs while sitting or put pressure on the back of the knees.
5) Refrain from smoking, especially for women who take family planning pills.
6) Drink at least 8 cups of fluids daily.
The diagnosis
Diagnosis of vein thrombosis is made by the clinical examination and the following tests:
1) Laboratory examination to find out the percentage of proteins and if there is a lack of some of them. If the deficiency is hereditary, the patient will need to take blood thinners throughout life.
2) The use of doppler ultrasound, which produces waves that show the movement of blood in the veins, and thus indicate the location of the clot in the deep veins. And the importance of ultrasound is that it is diagnostic and is used to monitor the patient's condition.
3) Catheterization of the veins by injecting a dye material into the vein to be examined (Venography).
4) Measuring changes in the amount of blood in the veins that result from a change in pressure (Plethysmography).
treatment
Venous thrombosis in deep veins is treated with blood-thinning medications, and these drugs may be given in the form of:
1) Intravenous injection, and here the patient may need to stay in the hospital during the treatment.
2) Injecting blood thinner under the skin in the abdomen or extremities.
3) Take pills according to what is prescribed by the treating physician, and as a result of this treatment the patient is monitored clinically and in the laboratory to see the percentage of blood thinning, so that it is from two to three times the rate in the average person.
4) The patient is injected with intravenous enzymes (Streptokinase and Urokinase).
Treatment goals
1) Prevention of pulmonary embolism.
2) stopping and dissolving the growth of a venous clot.
The duration of treatment usually ranges from three to six months, except for patients who have a tendency to clot. In this case, it is recommended to take liquids for life.
Dr. Abdullah Al-Qudah