Contents
- 1 What are the indications for a vacuum birth (aspiration or forceps)?
- 2 How common are they?
- 3 Can it be avoided?
- 4 What is scaling?
- 5 What is the fetal forceps?
- 6 What happens during childbirth?
- 7 Sizing or tweezers?
- 8 What are the factors that increase the failure rate of the forceps or forceps and increase the percentage of cesarean section?
- 9 What happens after birth?
- 10 What does a vacuum or forceps delivery mean for a patient?
- 11 What does a baby with volume or forceps mean to a child?
- 12 Care after discharge from the hospital?
- 13 Will I need forceps or drapery at the next delivery?
What are the indications for a vacuum birth (aspiration or forceps)?
There are several reasons, including the failure of the fetus to come out of the genital canal, the weak pulse of the fetus during labor, the inability of the woman to push the fetus due to her exhaustion, or the presence of certain diseases in her that prevent her from pushing it.
How common are they?
It is more common in the case of the first birth. Its prevalence varies from country to country, hospital to hospital, doctor to doctor, and according to the patient.
Can it be avoided?
The incidence can be reduced with psychological support and analgesics during labor, by avoiding the sitting position during labor, or in the position of lying on the side (right or left), by avoiding the back needle to relieve labor pain and by avoiding the repeated pushing of the fetus, and it can also be reduced by the use of artificial labor (drug induction of intravenous labor).
What is scaling?
A soft, soft or stiff device placed on the head of the fetus causes negative air pressure to stick to the head and thus enables the doctor to pull it during uterine contractions.
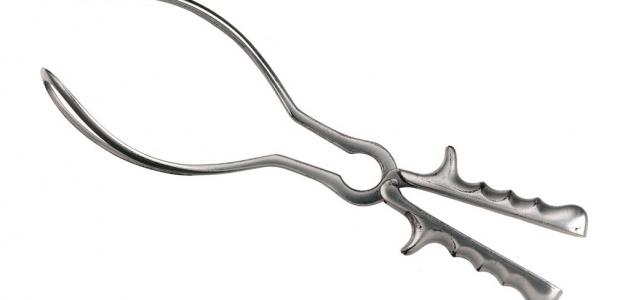
What is the fetal forceps?
A soft, stiff device is placed around the head of the fetus on both sides, so it grasps it, corresponding to the contours of the head. The head is pulled during uterine contractions.
Does the patient agree to apply the vacuum or forceps?
Necessary, verbal, and attested by those present at the time of birth, including doctors, nurses, and others. Often the doctor asks for this type of childbirth due to the interest of the mother or the interest of the fetus, or for other reasons that the doctor deems appropriate.
The choice of a forceps or a forceps is based on the opinion of the doctor and his experience, and the availability of either of them.
What happens during childbirth?
The abdomen will be examined, a vaginal examination, bladder emptying and topical or midline analgesic will be administered. Depending on the situation, the vulva may be biopsied (enlarging the outlet of the vagina).
Sized or tweezers?
They are both effective and safe and of many types. Forceps may be more successful in delivering the baby, but the diaphragm is safer to prevent tears in the vaginal wall.
It is not suitable to use a vacuum before the middle of the eighth month of pregnancy due to the tenderness of the head bones, the increased rate of bruising or bleeding in the brain, and the occurrence of jaundice (yellowing of the skin).
What are the factors that increase the failure rate of the forceps or forceps and increase the percentage of cesarean section?
Weight gain of a pregnant woman or fetus
That the back of the fetus is facing the mother's back
The head is high in the genital tract
- Technical failure in the vacuum device in all its parts
Lack of experience in the physician's correct use
Lack of cooperation of the patient
What happens after giving birth?
The baby should be taken care of by the pediatrician present in the delivery room at the time of delivery.
What does a vacuum or forceps delivery mean for the patient?
Bleeding is heavier than normal, but it will return to normal within days
- Tears in the vagina are more than normal and must be stitched. Severe lacerations increase after placement (four times) and forceps (10 times) after childbirth without them
Pain is more than natural childbirth and is treated with traditional painkillers
Bowel and bladder care: Problems with defecation or urination are common during the first days and disappear later
Clots in the legs: they increase in pregnancy and increase more when using a vacuum or forceps, which necessitates early movement, wearing appropriate rubber socks, or even taking needles to thin the blood
What does a baby with size or forceps mean for a child?
- Drainage leaves a prominent mark on the child's head that will disappear within two days and may cause blood to collect in the scalp, causing jaundice for a few days.
- The forceps usually leave a trace on the face of the fetus and it disappears within two days and may leave superficial wounds on the face or on the scalp that heal quickly and leave no trace.
Care after discharge from the hospital?
General and topical analgesics + blood tonics (minerals and vitamins) + baths of the genital area may be required + ice bags to reduce gynecological swelling, if any
Will I need forceps or cuffs for the next birth?
Probably not
Dr. Abdel Raouf Riad