Contents
Gallbladder
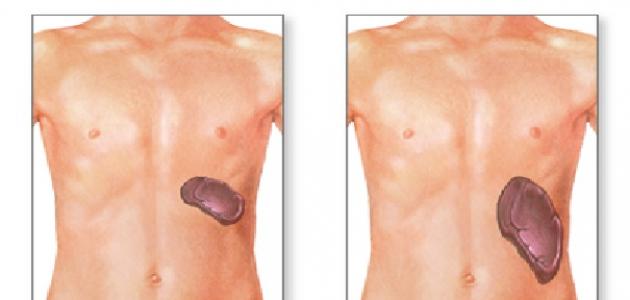
The gallbladder is a small, muscular organ with a cavity similar in shape to a pear, located under the liver in the right side of the upper part of the abdomen. Brown contains lipid-digesting enzymes, which are produced by the liver; To help the body absorb nutrients and fat- soluble vitamins . [1] [2] [3]
After eating, the intestinal cells produce a hormone called cholecystokinin, which stimulates the gallbladder to secrete bile into the small intestine through the common bile duct, and it also drains liver waste into a part of the small intestine Ten . [1] [2]
Gallbladder diseases
Gallstones
Gallstones is a deposition calloused formed in the gallbladder as a result of the crystallization of substances found in the yellow material in the gallbladder or not as a result of the completion of unloading the gall bladder full or adequate manner. They are usually small in size, not exceeding a few millimeters, but they can grow in size up to several centimeters. As the stones increase in size, the ducts that exit the gallbladder may block and lead to problems including pain and inflammation. [4] [5] [6]
The main types of gallstones are: [7] [4]
- Cholesterol stone : the most common type of cholesterol present in the bile, and it is often greenish-yellow in color.
- Pigment stone: the less common type consisting of bilirubin and calcium salts such as calcium bilirubinate ; The substance produced by the breakdown of red blood cells.
In addition to the fact that females are more vulnerable to gallstones, there are many factors that increase the risk of developing gallstones, including: [6] [7]
- Obesity.
- Disease diabetes .
- Age; Sixty years or more.
- Take medications that contain estrogen.
- Take cholesterol-lowering medications.
- Lose weight quickly.
- A family history of gallstones.
Inflammation of the gallbladder
There are two types of cholecystitis : [1] [6]
- Acute cholecystitis: occurs as a result of a blockage in the ducts of the gallbladder, and thus the bile substance is prevented from leaving the gallbladder, and the cause is often the presence of gallstones, and this is accompanied by pain after eating directly in the upper right or middle part of the abdomen .
- Chronic cholecystitis: occurs as a result of repeated bouts of acute inflammation, and then the gallbladder shrinks and loses its ability to store and excrete the bile substance.
Stones of the common bile duct
The presence of stones inside the common bile ducts, which connect between the gallbladder and the small intestine. Stones within the channel itself, and are called primary stones, and this type often causes infections. [4]
Non-gallstone disease
Disease gallbladder is gravel is an inflammation of the gallbladder without the presence of kidney stones in, and there are many factors may cause the occurrence of heart and abdomen as processes, burns and other difficult. [6]
Gallbladder cancer
Gallbladder cancer is a rare disease , and it is often diagnosed in advanced stages of the disease , and thus it becomes difficult to treat. Symptoms may resemble acute cholecystitis, and symptoms may never appear, and if not treated, the disease spreads to other channels and organs. [6]
Benign gallbladder tumors
Gallbladder polyps are benign, non- cancerous growths in the gallbladder, which may be small in size and do not pose a threat to the gallbladder, and therefore there is no need to remove them, but if they are large, they must be surgically removed to avoid other problems or cancerous growth . [4]
Gangrene or gallbladder erosions
Gangrene of the gallbladder occurs when blood flow to the gallbladder is ineffective and is one of the most common complications of cholecystitis. Among the factors that contribute to its occurrence: Diabetes and others. [6]
Gall bladder abscess
Gallbladder abscess , which is pus or pus inside the gallbladder consisting of white blood cells, bacteria and dead cells, accompanied by severe pain in the abdomen, and it occurs in a small percentage of those who suffer from gallstones. If left untreated, this condition becomes life-threatening and the infection spreads to other parts of the body. [4]
Perforated gallbladder
Perforated gallbladder , if gallstones are not treated for a long time, this may result in a perforated gallbladder, and this condition is considered dangerous as it can lead to widespread inflammation in the abdomen. [4]
Ceramic gallbladder
The ceramic gallbladder , the natural gallbladder contains muscle walls, while with the passage of time the walls become stiffer due to calcium deposits on them, and those who suffer from this problem are considered to be more vulnerable than others to gallbladder cancer . [4]
Symptoms associated with gallbladder disease
The following are the main symptoms associated with gallbladder disease: [1] [4]
- Pain: The most common symptom of gallbladder disease is usually located in the upper right and middle part of the abdomen, and may sometimes extend to the back or chest, and the pain ranges between mild intermittent and severe continuous.
- Nausea and vomiting: This is a common symptom of all gallbladder diseases.
- Heat or cold chills: This is usually a sign of infection. It must be treated before it spreads to other parts of the body, and thus becomes life-threatening.
- Chronic diarrhea: An active bowel movement - that is, more than four times a day for at least three months - indicates the presence of a chronic disease of the gallbladder.
- Jaundice : yellowing of the skin that usually occurs as a result of blockage of the bile duct in front of the yellow substance coming from the liver towards the intestine, as a result of the presence of gallstones or a problem in the liver.
- Change in the color of stool and urine: A change in the color of stools to a light color, and urine to a dark color, may be caused by a blockage of the bile duct.
Diagnosis of gallbladder diseases
To diagnose gallbladder diseases, the doctor performs one or more of the following procedures and examinations: [1] [5] [6]
- The patient's medical history: a list of the symptoms that the patient had previously suffered in addition to a family history of gallbladder disease.
- Physical examination: The doctor uses a special method to examine the abdominal area clinically, which consists in placing his hand on the gallbladder and pressing, then asking the patient to breathe to notice the Murphy's sign, and if the patient feels severe pain, there is a high possibility of a problem in the gallbladder.
- Abdominal x-ray imaging: (X-ray) Sometimes gallstones, especially calcium-containing, are visible during the X-ray imaging.
- Blood tests: It relies on blood tests such as white blood cells count , and an examination of liver function, as their elevation indicates the presence of inflammation in the bile duct or pancreas.
- Abdominal ultrasound: is a non-invasive examination that is performed using high-frequency sound waves that produce an image of the gallbladder that shows the presence of stones or an increase in the thickness of the walls in the gallbladder.
- Magnetic Resonance Cholangiography ( MRCP ) : ; Using magnetic resonance imaging technology, a high-resolution image of the gallbladder, duct, bile duct, and pancreas is obtained.
- The HIDA scan of the biliary system: is done using a radioactive dye that is injected into the vein and then secreted with the yellow substance, and by observing the movement of the radioactive dye, the presence of gallbladder inflammation is confirmed.
- ERCP: Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography, using a flexible tube inserted from the mouth, through the stomach, to the intestine, and then a dye is injected into the bile ducts through the tube. With this technique, it is possible to treat some cases of gallstones.
Treating gallbladder diseases
Treatment options include the following: [5] [6]
- Use of antibiotics and painkillers: If the patient suffers from inflammation of the gallbladder without the presence of stones, antibiotics are used to prevent the spread of the infection.
- Use of ursodeoxycholic acid: This drug is used in patients with gallstones, and it is not appropriate to undergo surgery for them, as the drug helps to break up small-sized cholesterol stones and reduce symptoms.
- Lithotripsy shock waves: are using shocking waves of high power shed on the abdominal wall of the fragmentation of gravel and small bile.
- Surgery: the surgical option is sometimes appropriate for the case, and it is done either in the traditional way by making a large opening in the abdomen or by laparoscopy by making three openings in the abdomen and inserting a camera, and doctors prefer the second method For the quick and easy recovery of the patient and the lack of scars. In general, cholecystectomy does not cause significant digestive problems, but it can lead to minor problems such as diarrhea and poor absorption of fats.
References
- ^ A b t w c of Jenna of Fletcher (27-2-2017), "The Know View And Symptoms Of of signs Gallbladder Problems" , Medical News the Today , Retrieved 6-8-2017. Edited
- ^ A b Healthline Medical the Team (3-12-2014), "Gallbladder" , Healthline , Retrieved 6-8-2017. Edited
- ↑ Tim Taylor, "Gallbladder" , Inner Body , Retrieved 6-8-2017. Edited
- ^ A b t w c h x d Kimberly Holland (17-7-2017), "Identifying Gallbladder Problems And the Symptoms" , Healthline , Retrieved 6-8-2017. Edited
- ^ A b v . Matthew Hoffman 's (11-3-2017), " the Picture Of The Gallbladder" , the Web MD , Retrieved 6-8-2017. Edited
- ^ A b t w c h x d Azouz And Wadood Mohamed Mohamed 's. Matthew Solan (23-10-2015), "Gallbladder Disease" , Healthline , Retrieved 6-8-2017. Edited
- ^ A b , David T . Derrer (27-2-2016), "Gallstones: What ' You Should Know View " , the Web MD , Retrieved 6-8-2017. Edited