Contents
ovulation
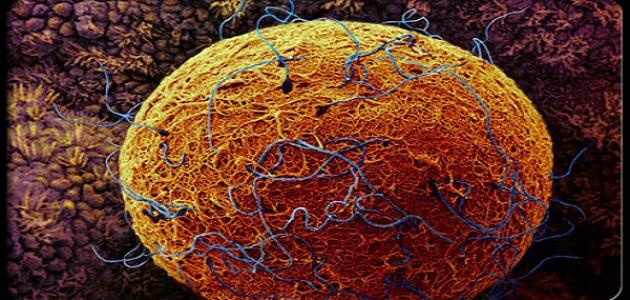
Ovaries are considered part of the female reproductive system, and the female is born with millions of immature eggs in her ovaries, then one egg matures every month from one of the ovaries, and after it reaches and completes its maturity it is released from the ovary towards the fallopian tube to wait for the animal The seminal process for fertilization to occur, this process is known as ovulation , and it is worth noting that the egg is able to survive for approximately 12-24 hours from the moment it leaves the ovary, and at the same time the body, through its female hormones, prepares the lining of the uterus to increase its thickness in preparation for implantation. Thus, the pregnancy process begins, But in cases where fertilization does not occur, the uterine lining sheds during a process known as menstrual bleeding (menstrual cycle). It is worth noting that ovulation may occur even in the absence of a period. [1]
How does ovulation occur
It can be said that the ovulation process is the stage in which hormones rise during the menstrual cycle, and this stage can be classified into three phases, and the following is a statement: [2] [1]
- The proliferative phase: or the follicular phase, and in this phase, a layer of cells surrounding the egg begins to expand and becomes similar to mucus, and at the same time the endometrium begins to thicken. It is worth noting that this phase starts from the first day of the last menstruation and continues until ovulation.
- The ovulation phase: , this phase lasts from 24 to 48 hours, in which enzymes are secreted, and a cavity is formed that the egg uses with its cells to reach the fallopian tube, and this phase is the one that represents the fertile period of a woman. It can be said that the day of ovulation is what determines the period and length of the menstrual cycle.
- The postovulatory phase or the luteal phase , and this phase is known by this name because in it the hormone known as the luteinizing hormone is secreted, and in this phase the fertilized egg implants in the uterus , While the unfertilized egg is shed and the body gets rid of it within twenty-four hours, the lining of the uterus begins to prepare to be shed during the period of menstrual bleeding. It should be noted that the luteal phase ranges from 12 to 16 days from the time of ovulation.
The time of ovulation
It can be said that the menstrual cycle begins on the first day of the bleeding of the period and continues to the first day of the subsequent period bleeding, and this period ranges in normal cases between 28 to 32 days, and this does not preclude the possibility that the cycle is shorter or longer than that for some women. The time of ovulation can be known by looking at the first day of the last menstrual cycle, where the day of ovulation is usually between the eleventh and twenty-first days, and in another way, the day of ovulation can be known by looking at the expected date of the subsequent menstrual cycle, usually during the extended period Between the twelfth and sixteenth day. To better illustrate the time of ovulation, we can assume a condition and calculate the time based on it, for example if it is your periodThey are usually organized to be 28 days. The day of ovulation is expected to be the fourteenth day, which represents the middle of the menstrual cycle, and the woman is often fertile during the period between the tenth day and the fourteenth day. It should be noted that the day of ovulation may differ from one cycle to the next, but it is important to know that the time of ovulation represents the period in which a woman is at the highest levels of fertility and then the probability of pregnancy increases if fertilization is complete. [1] [3]
Signs of ovulation
Some women do not show any signs of ovulation, and on the other hand some signs may appear on each other, and among these signs we mention the following: [4]
- Feeling of cramping .
- Sensation of pain in the breast.
- Flatulence
- Increase sexual desire.
- Noticing a change in the cervical fluid, it may become similar in appearance to egg white, and it is worth noting that this indicates that this day is the day of ovulation or that ovulation is about to occur during the next few days.
- An increase in the basal body temperature, which is defined as the body temperature at rest, but despite this rise during ovulation, some women notice that a rise in their basic body temperature occurs after the period of ovulation or Fertility is two to three days.
There are some health disorders related to ovulation, may entail women 's suffering from some complications , including infertility , mention of these problems as follows: [2]
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome: It is defined as an increase in the size of the ovaries with small fluid-filled sacs on the ovaries.
- Hypothalamic disorders: , and these disorders are represented by an imbalance of the level of the follicle-stimulating hormone and the luteinizing hormone.
- Early ovarian failure: , and Acronym (POF), expressed as a result of stopping the process of ovulation decline in the level of the hormone estrogen , and often this failure occurs in women who are not over the age of forty years.
- Hyperprolactinemia: , and although this disorder is considered an uncommon condition for suffering from ovulation problems, it is possible, and it is often represented by a problem in the pituitary gland that secretes prolactin known as the milk hormone or taking drugs that affect the level of prolactin in general.
References
- ^ A b v "Understanding Ovulation" , Americanpregnancy.org , Retrieved April 13, 2018. Edited by .
- ^ A b "Everything You Need To Know About Ovulation" , www.medicalnewstoday.com The , Retrieved April 13, 2018. Edited by .
- ↑ "Am I Ovulating?" , www.webmd.com , Retrieved April 13, 2018. Edited.
- ↑ "How Long Does Ovulation Last Each Month?" , www.healthline.com , Retrieved April 13, 2018. Edited.